Protection against a mixed SHIV challenge by a broadly neutralizing antibody cocktail
- PMID: 28931655
- PMCID: PMC5747528
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aao4235
Protection against a mixed SHIV challenge by a broadly neutralizing antibody cocktail
Abstract
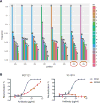
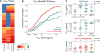
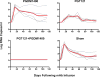
HIV-1 sequence diversity presents a major challenge for the clinical development of broadly neutralizing antibodies (bNAbs) for both therapy and prevention. Sequence variation in critical bNAb epitopes has been observed in most HIV-1-infected individuals and can lead to viral escape after bNAb monotherapy in humans. We show that viral sequence diversity can limit both the therapeutic and prophylactic efficacy of bNAbs in rhesus monkeys. We first demonstrate that monotherapy with the V3 glycan-dependent antibody 10-1074, but not PGT121, results in rapid selection of preexisting viral variants containing N332/S334 escape mutations and loss of therapeutic efficacy in simian-HIV (SHIV)-SF162P3-infected rhesus monkeys. We then show that the V3 glycan-dependent antibody PGT121 alone and the V2 glycan-dependent antibody PGDM1400 alone both fail to protect against a mixed challenge with SHIV-SF162P3 and SHIV-325c. In contrast, the combination of both bNAbs provides 100% protection against this mixed SHIV challenge. These data reveal that single bNAbs efficiently select resistant viruses from a diverse challenge swarm to establish infection, demonstrating the importance of bNAb cocktails for HIV-1 prevention.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
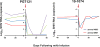


References
-
- Bar KJ, Sneller MC, Harrison LJ, Justement JS, Overton ET, Petrone ME, Salantes DB, Seamon CA, Scheinfeld B, Kwan RW, Learn GH, Proschan MA, Kreider EF, Blazkova J, Bardsley M, Refsland EW, Messer M, Clarridge KE, Tustin NB, Madden PJ, Oden K, O’Dell SJ, Jarocki B, Shiakolas AR, Tressler RL, Doria-Rose NA, Bailer RT, Ledgerwood JE, Capparelli EV, Lynch RM, Graham BS, Moir S, Koup RA, Mascola JR, Hoxie JA, Fauci AS, Tebas P, Chun TW. Effect of HIV Antibody VRC01 on Viral Rebound after Treatment Interruption. The New England journal of medicine. 2016;375:2037–2050. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Scheid JF, Horwitz JA, Bar-On Y, Kreider EF, Lu CL, Lorenzi JC, Feldmann A, Braunschweig M, Nogueira L, Oliveira T, Shimeliovich I, Patel R, Burke L, Cohen YZ, Hadrigan S, Settler A, Witmer-Pack M, West AP, Jr, Juelg B, Keler T, Hawthorne T, Zingman B, Gulick RM, Pfeifer N, Learn GH, Seaman MS, Bjorkman PJ, Klein F, Schlesinger SJ, Walker BD, Hahn BH, Nussenzweig MC. HIV-1 antibody 3BNC117 suppresses viral rebound in humans during treatment interruption. Nature. 2016;535:556–560. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Caskey M, Klein F, Lorenzi JC, Seaman MS, West AP, Jr, Buckley N, Kremer G, Nogueira L, Braunschweig M, Scheid JF, Horwitz JA, Shimeliovich I, Ben-Avraham S, Witmer-Pack M, Platten M, Lehmann C, Burke LA, Hawthorne T, Gorelick RJ, Walker BD, Keler T, Gulick RM, Fatkenheuer G, Schlesinger SJ, Nussenzweig MC. Viraemia suppressed in HIV-1-infected humans by broadly neutralizing antibody 3BNC117. Nature. 2015;522:487–491. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

