Emerging therapies for acute myeloid leukemia: translating biology into the clinic
- PMID: 28931762
- PMCID: PMC5621868
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.95679
Emerging therapies for acute myeloid leukemia: translating biology into the clinic
Abstract
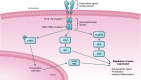
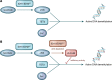
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is an aggressive hematological malignancy with a poor outcome; overall survival is approximately 35% at two years and some subgroups have a less than 5% two-year survival. Recently, significant improvements have been made in our understanding of AML biology and genetics. These fundamental discoveries are now being translated into new therapies for this disease. This review will discuss recent advances in AML biology and the emerging treatments that are arising from biological studies. Specifically, we will consider new therapies that target molecular mutations in AML and dysregulated pathways such as apoptosis and mitochondrial metabolism. We will also discuss recent advances in immune and cellular therapy for AML.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent advances in the understanding and treatment of acute myeloid leukemia.F1000Res. 2018 Aug 6;7:F1000 Faculty Rev-1196. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.14116.1. eCollection 2018. F1000Res. 2018. PMID: 30135719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular targeting in acute myeloid leukemia.J Transl Med. 2017 Aug 29;15(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s12967-017-1281-x. J Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28851395 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An expert overview of emerging therapies for acute myeloid leukemia: novel small molecules targeting apoptosis, p53, transcriptional regulation and metabolism.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020 Sep;29(9):973-988. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2020.1804856. Epub 2020 Aug 17. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32746655 Review.
-
The Evolving AML Genomic Landscape: Therapeutic Implications.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2020;20(7):532-544. doi: 10.2174/1568009620666200424150321. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 32329691 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular-Targeted Therapy of Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Molecules. 2022 Jun 18;27(12):3911. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123911. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35745032 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deoxyshikonin Inhibits Viability and Glycolysis by Suppressing the Akt/mTOR Pathway in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells.Front Oncol. 2020 Aug 7;10:1253. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01253. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32850379 Free PMC article.
-
Niclosamide suppresses acute myeloid leukemia cell proliferation through inhibition of CREB-dependent signaling pathways.Oncotarget. 2017 Dec 31;9(4):4301-4317. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23794. eCollection 2018 Jan 12. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29435104 Free PMC article.
-
RSK Isoforms in Acute Myeloid Leukemia.Biomedicines. 2021 Jun 24;9(7):726. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070726. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34202904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences of basic and induced autophagic activity between K562 and K562/ADM cells.Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2017 Nov;6(4):281-290. doi: 10.5582/irdr.2017.01069. Intractable Rare Dis Res. 2017. PMID: 29259857 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase induces apoptosis and differentiation in acute myeloid leukemia cells.Haematologica. 2018 Sep;103(9):1472-1483. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2018.188185. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Haematologica. 2018. PMID: 29880605 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

