Improvement of a fermentation process for the production of two PfAMA1-DiCo-based malaria vaccine candidates in Pichia pastoris
- PMID: 28931852
- PMCID: PMC5607246
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-11819-4
Improvement of a fermentation process for the production of two PfAMA1-DiCo-based malaria vaccine candidates in Pichia pastoris
Abstract
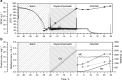
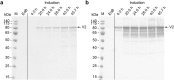
Pichia pastoris is a simple and powerful expression platform that has the ability to produce a wide variety of recombinant proteins, ranging from simple peptides to complex membrane proteins. A well-established fermentation strategy is available comprising three main phases: a batch phase, followed by a glycerol fed-batch phase that increases cell density, and finally an induction phase for product expression using methanol as the inducer. We previously used this three-phase strategy at the 15-L scale to express three different AMA1-DiCo-based malaria vaccine candidates to develop a vaccine cocktail. For two candidates, we switched to a two-phase strategy lacking the intermediate glycerol fed-batch phase. The new strategy not only provided a more convenient process flow but also achieved 1.5-fold and 2.5-fold higher space-time yields for the two candidates, respectively, and simultaneously reduced the final cell mass by a factor of 1.3, thus simplifying solid-liquid separation. This strategy also reduced the quantity of host cell proteins that remained to be separated from the two vaccine candidates (by 34% and 13%, respectively), thus reducing the effort required in the subsequent purification steps. Taken together, our new fermentation strategy increased the overall fermentation performance for the production of two different AMA1-DiCo-based vaccine candidates.
Conflict of interest statement
A.B., H.S., A.R., and R.F. have filed a patent on multistage malaria vaccines (EP14183995.1,US-provisional US62/047,286). The other authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Cereghino, J. L. & Cregg, J. M. Heterologous protein expression in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 24, 45–66, doi:S0168-6445(99)00029-7 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

