THP-1-derived macrophages render lung epithelial cells hypo-responsive to Legionella pneumophila - a systems biology study
- PMID: 28931863
- PMCID: PMC5607273
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12154-4
THP-1-derived macrophages render lung epithelial cells hypo-responsive to Legionella pneumophila - a systems biology study
Abstract
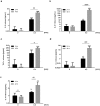
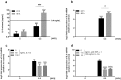
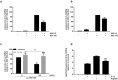
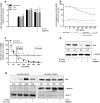
Immune response in the lung has to protect the huge alveolar surface against pathogens while securing the delicate lung structure. Macrophages and alveolar epithelial cells constitute the first line of defense and together orchestrate the initial steps of host defense. In this study, we analysed the influence of macrophages on type II alveolar epithelial cells during Legionella pneumophila-infection by a systems biology approach combining experimental work and mathematical modelling. We found that L. pneumophila-infected THP-1-derived macrophages provoke a pro-inflammatory activation of neighboring lung epithelial cells, but in addition render them hypo-responsive to direct infection with the same pathogen. We generated a kinetic mathematical model of macrophage activation and identified a paracrine mechanism of macrophage-secreted IL-1β inducing a prolonged IRAK-1 degradation in lung epithelial cells. This intercellular crosstalk may help to avoid an overwhelming inflammatory response by preventing excessive local secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines and thereby negatively regulating the recruitment of immune cells to the site of infection. This suggests an important but ambivalent immunomodulatory role of macrophages in lung infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Legionella pneumophila infection activates bystander cells differentially by bacterial and host cell vesicles.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 24;7(1):6301. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06443-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28740179 Free PMC article.
-
Alveolar macrophage cell line MH-S is valuable as an in vitro model for Legionella pneumophila infection.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001 Mar;24(3):326-31. doi: 10.1165/ajrcmb.24.3.4359. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11245632
-
PilY1 Promotes Legionella pneumophila Infection of Human Lung Tissue Explants and Contributes to Bacterial Adhesion, Host Cell Invasion, and Twitching Motility.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017 Mar 7;7:63. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00063. eCollection 2017. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28326293 Free PMC article.
-
Innate immunity against Legionella pneumophila during pulmonary infections in mice.Arch Pharm Res. 2017 Feb;40(2):131-145. doi: 10.1007/s12272-016-0859-9. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Arch Pharm Res. 2017. PMID: 28063015 Review.
-
Programmed cell death in Legionella infection.Future Microbiol. 2014;9(1):107-18. doi: 10.2217/fmb.13.139. Future Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24328384 Review.
Cited by
-
Host-microbe cross-talk in the lung microenvironment: implications for understanding and treating chronic lung disease.Eur Respir J. 2020 Aug 20;56(2):1902320. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02320-2019. Print 2020 Aug. Eur Respir J. 2020. PMID: 32430415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of precision cut lung slices as a translational model for the study of lung biology.Respir Res. 2019 Jul 19;20(1):162. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1131-x. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 31324219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multi-Level Computational Modeling of Anti-Cancer Dendritic Cell Vaccination Utilized to Select Molecular Targets for Therapy Optimization.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Feb 2;9:746359. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.746359. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35186943 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial vesicles block viral replication in macrophages via TLR4-TRIF-axis.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Mar 28;21(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01086-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36978183 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Age, Neutrophil Infiltration and Antibiotics Timing in the Severity of Streptococcus pneumoniae Pneumonia. Insights from a Multi-Level Mathematical Model Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 10;21(22):8428. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228428. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33182614 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO. Pneumonia (2015).
-
- Wardlaw, T., White Johansson, E. & Hodge M. Pneumonia: The forgotten killer of children. (UNICEF/WHO 2006).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

