A method to identify trace sulfated IgG N-glycans as biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 28931878
- PMCID: PMC5606999
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00662-w
A method to identify trace sulfated IgG N-glycans as biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
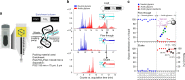
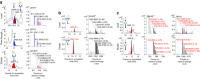
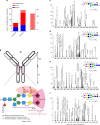
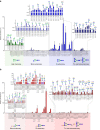
N-linked glycans on immunoglobulin G (IgG) have been associated with pathogenesis of diseases and the therapeutic functions of antibody-based drugs; however, low-abundance species are difficult to detect. Here we show a glycomic approach to detect these species on human IgGs using a specialized microfluidic chip. We discover 20 sulfated and 4 acetylated N-glycans on IgGs. Using multiple reaction monitoring method, we precisely quantify these previously undetected low-abundance, trace and even ultra-trace N-glycans. From 277 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and 141 healthy individuals, we also identify N-glycan biomarkers for the classification of both rheumatoid factor (RF)-positive and negative RA patients, as well as anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA)-positive and negative RA patients. This approach may identify N-glycosylation-associated biomarkers for other autoimmune and infectious diseases and lead to the exploration of promising glycoforms for antibody therapeutics.Post-translational modifications can affect antibody function in health and disease, but identification of all variants is difficult using existing technologies. Here the authors develop a microfluidic method to identify and quantify low-abundance IgG N-glycans and show some of these IgGs can be used as biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Rheumatoid arthritis: Seronegative RA-specific biomarkers identified.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017 Nov;13(11):633. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.166. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28978990 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
N-Linked Glycans in the Variable Domain of IgG Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibodies Predict the Development of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019 Oct;71(10):1626-1633. doi: 10.1002/art.40920. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 31067000 Free PMC article.
-
IgG antibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides exhibit profiles specific in terms of IgG subclasses, Fc-glycans and a fab-Peptide sequence.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 26;9(11):e113924. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0113924. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25426976 Free PMC article.
-
On the presence of HLA-SE alleles and ACPA-IgG variable domain glycosylation in the phase preceding the development of rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Rheum Dis. 2019 Dec;78(12):1616-1620. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215698. Epub 2019 Aug 30. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019. PMID: 31471298
-
Meta-analysis: diagnostic accuracy of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Intern Med. 2007 Jun 5;146(11):797-808. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-146-11-200706050-00008. Ann Intern Med. 2007. PMID: 17548411 Review.
-
The Emerging Importance of IgG Fab Glycosylation in Immunity.J Immunol. 2016 Feb 15;196(4):1435-41. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1502136. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26851295 Review.
Cited by
-
A Study on COMP and CTX-II as Molecular Markers for the Diagnosis of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Aug 3;2021:3371091. doi: 10.1155/2021/3371091. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34395611 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated level of multibranched complex glycan reveals an allergic tolerance status.Clin Proteomics. 2024 Jun 8;21(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12014-024-09491-8. Clin Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 38849742 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Characterization of N-Linked Glycans in the Receptor Binding Domain of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein and their Interactions with Human Lectins.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Dec 21;59(52):23763-23771. doi: 10.1002/anie.202011015. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32915505 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of N-glycan Biomarkers for the Canine Osteoarthritis.Life (Basel). 2020 Sep 14;10(9):199. doi: 10.3390/life10090199. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32937769 Free PMC article.
-
Reliable N-Glycan Analysis-Removal of Frequently Occurring Oligosaccharide Impurities by Enzymatic Degradation.Molecules. 2023 Feb 15;28(4):1843. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041843. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838829 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

