A method to identify trace sulfated IgG N-glycans as biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 28931878
- PMCID: PMC5606999
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-00662-w
A method to identify trace sulfated IgG N-glycans as biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
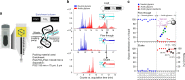
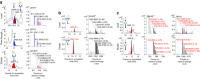
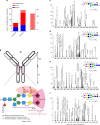
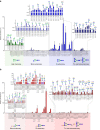
N-linked glycans on immunoglobulin G (IgG) have been associated with pathogenesis of diseases and the therapeutic functions of antibody-based drugs; however, low-abundance species are difficult to detect. Here we show a glycomic approach to detect these species on human IgGs using a specialized microfluidic chip. We discover 20 sulfated and 4 acetylated N-glycans on IgGs. Using multiple reaction monitoring method, we precisely quantify these previously undetected low-abundance, trace and even ultra-trace N-glycans. From 277 patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and 141 healthy individuals, we also identify N-glycan biomarkers for the classification of both rheumatoid factor (RF)-positive and negative RA patients, as well as anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA)-positive and negative RA patients. This approach may identify N-glycosylation-associated biomarkers for other autoimmune and infectious diseases and lead to the exploration of promising glycoforms for antibody therapeutics.Post-translational modifications can affect antibody function in health and disease, but identification of all variants is difficult using existing technologies. Here the authors develop a microfluidic method to identify and quantify low-abundance IgG N-glycans and show some of these IgGs can be used as biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Rheumatoid arthritis: Seronegative RA-specific biomarkers identified.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017 Nov;13(11):633. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.166. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28978990 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

