Cytochalasan and Tyrosine-Derived Alkaloids from the Marine Sediment-Derived Fungus Westerdykella dispersa and Their Bioactivities
- PMID: 28931947
- PMCID: PMC5607321
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12327-1
Cytochalasan and Tyrosine-Derived Alkaloids from the Marine Sediment-Derived Fungus Westerdykella dispersa and Their Bioactivities
Abstract
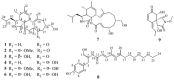
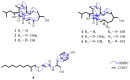
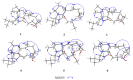
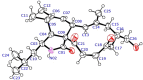
Six new cytochalasans, designated as 18-oxo-19,20-dihydrophomacin C (1), 18-oxo-19-methoxy-19,20- dihydrophomacin C (2), 18-oxo-19-hydroxyl-19,20-dihydrophomacin C (3), 19,20-dihydrophomacin C (4), 19-methoxy-19,20-dihydrophomacin C (5), 19-hydroxyl-19,20-dihydrophomacin C (6), and one new tyrosine-derived alkaloid named as gymnastatin Z (8), together with two known compounds, phomacin B (7) and triticone D (9), were isolated from a solid-substrate fermentation culture of Westerdykella dispersa which was derived from marine sediments. Their structures were established on the basis of spectroscopic analysis using 1D and 2D NMR techniques, and comparison of NMR data to those of known compounds. The anti-bacterial and cytotoxic activities assays of all isolated compounds were evaluated against eight human pathogenic bacteria and five human cancer cell lines, respectively. Compound 8 exhibited moderate activity against B. subtilis with MIC values of 12.5 µg/mL, while compounds 5, 7 and 8 displayed moderate inhibitory activities against five human cancer cell lines (MCF-7, HepG2, A549, HT-29 and SGC-7901), with IC50 values ranging from 25.6 to 83.7 µM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive Overview on the Chemistry and Biological Activities of Selected Alkaloid Producing Marine-Derived Fungi as a Valuable Reservoir of Drug Entities.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 28;9(5):485. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050485. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33925060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive Pyridone Alkaloids from a Deep-Sea-Derived Fungus Arthrinium sp. UJNMF0008.Mar Drugs. 2018 May 22;16(5):174. doi: 10.3390/md16050174. Mar Drugs. 2018. PMID: 29786655 Free PMC article.
-
New alkenylated tetrahydropyran derivatives from the marine sediment-derived fungus Westerdykella dispersa and their bioactivities.Fitoterapia. 2017 Oct;122:45-51. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2017.08.010. Epub 2017 Aug 23. Fitoterapia. 2017. PMID: 28842357
-
Two new stemphol sulfates from the mangrove endophytic fungus Stemphylium sp. 33231.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2015 Aug;68(8):501-3. doi: 10.1038/ja.2015.16. Epub 2015 Feb 25. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2015. PMID: 25712398
-
An insight into purine, tyrosine and tryptophan derived marine antineoplastic alkaloids.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015;15(8):947-54. doi: 10.2174/1871520615666150101143520. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25553433 Review.
Cited by
-
Fungal frontiers in toxic terrain: Revealing culturable fungal communities in Serpentine paddy fields of Taiwan.IMA Fungus. 2025 Jun 27;16:e155308. doi: 10.3897/imafungus.16.155308. eCollection 2025. IMA Fungus. 2025. PMID: 40822984 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Alkaloids from Marine-Derived Fungi as Drug Leads versus COVID-19 Infection: A Computational Approach to Explore their Anti-COVID-19 Activity and ADMET Properties.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jul 8;2022:5403757. doi: 10.1155/2022/5403757. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35911157 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in the Chemistry of Cytochalasans.Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2021;114:1-134. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-59444-2_1. Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2021. PMID: 33792860
-
Comprehensive Overview on the Chemistry and Biological Activities of Selected Alkaloid Producing Marine-Derived Fungi as a Valuable Reservoir of Drug Entities.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 28;9(5):485. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9050485. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33925060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biotic Interactions Are More Important than Propagule Pressure in Microbial Community Invasions.mBio. 2020 Oct 27;11(5):e02089-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02089-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33109758 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Michael B, Christoph T. Nomenclature of a class of biologically active mould metabolites: the cytochalasins, phomins, and zygosporins. J. Chem. Soc., Perkin Trans. 1973;1:1146–1147. - PubMed
-
- Rothweiler W, Tamm C. Isolation and structure of phomin. Experientia. 1966;22:750–752. doi: 10.1007/BF01901360. - DOI
-
- Aldridge DC, Armstrong JJ, Speake RN, Turner WB. The cytochalasins, a new class of biologically active mould metabolites. Chem. Commun. 1967;1:26–27.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical