Improving Acetic Acid Production by Over-Expressing PQQ-ADH in Acetobacter pasteurianus
- PMID: 28932219
- PMCID: PMC5592214
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01713
Improving Acetic Acid Production by Over-Expressing PQQ-ADH in Acetobacter pasteurianus
Abstract
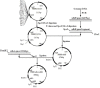
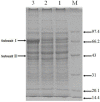
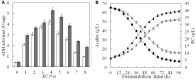
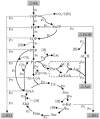
Pyrroquinoline quinone-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase (PQQ-ADH) is a key enzyme in the ethanol oxidase respiratory chain of acetic acid bacteria (AAB). To investigate the effect of PQQ-ADH on acetic acid production by Acetobacter pasteurianus JST-S, subunits I (adhA) and II (adhB) of PQQ-ADH were over-expressed, the fermentation parameters and the metabolic flux analysis were compared in the engineered strain and the original one. The acetic acid production was improved by the engineered strain (61.42 g L-1) while the residual ethanol content (4.18 g L-1) was decreased. Analysis of 2D maps indicated that 19 proteins were differently expressed between the two strains; of these, 17 were identified and analyzed by mass spectrometry and two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. With further investigation of metabolic flux analysis (MFA) of the pathway from ethanol and glucose, the results reveal that over-expression of PQQ-ADH is an effective way to improve the ethanol oxidation respiratory chain pathway and these can offer theoretical references for potential mechanism of metabolic regulation in AAB and researches with its acetic acid resistance.
Keywords: Acetobacter pasteurianus JST-S; Pyrroquinoline quinone-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase; metabolic flux analysis; two-dimensional gel electrophoresis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Improving the alcohol respiratory chain and energy metabolism by enhancing PQQ synthesis in Acetobacter pasteurianus.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 9;51:kuae036. doi: 10.1093/jimb/kuae036. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39341788 Free PMC article.
-
Producing Acetic Acid of Acetobacter pasteurianus by Fermentation Characteristics and Metabolic Flux Analysis.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2018 Sep;186(1):217-232. doi: 10.1007/s12010-018-2732-4. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29552715
-
Cloning and functional analysis of adhS gene encoding quinoprotein alcohol dehydrogenase subunit III from Acetobacter pasteurianus SKU1108.Int J Food Microbiol. 2010 Mar 31;138(1-2):39-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2009.12.027. Epub 2010 Jan 11. Int J Food Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20096472
-
Pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent dehydrogenases of acetic acid bacteria.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Nov;102(22):9531-9540. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9360-3. Epub 2018 Sep 15. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30218379 Review.
-
Alcohol dehydrogenase of acetic acid bacteria: structure, mode of action, and applications in biotechnology.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010 May;86(5):1257-65. doi: 10.1007/s00253-010-2529-z. Epub 2010 Mar 20. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20306188 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhanced bacterial cellulose production in Komagataeibacter sucrofermentans: impact of different PQQ-dependent dehydrogenase knockouts and ethanol supplementation.Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024 Feb 29;17(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s13068-024-02482-9. Biotechnol Biofuels Bioprod. 2024. PMID: 38424558 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering Bacterial Cellulose by Synthetic Biology.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 2;21(23):9185. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239185. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33276459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
On the way toward regulatable expression systems in acetic acid bacteria: target gene expression and use cases.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 May;105(9):3423-3456. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11269-z. Epub 2021 Apr 15. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33856535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine-tuning ethanol oxidation pathway enzymes and cofactor PQQ coordinates the conflict between fitness and acetic acid production by Acetobacter pasteurianus.Microb Biotechnol. 2021 Mar;14(2):643-655. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.13703. Epub 2020 Nov 11. Microb Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33174682 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Strain Probiotics Enhance the Bioactivity of Cascara Kombucha during Microbial Composition-Controlled Fermentation.Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023 Dec 31;28(4):502-513. doi: 10.3746/pnf.2023.28.4.502. Prev Nutr Food Sci. 2023. PMID: 38188087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y., Bai Y., Li D., Wang C., Xu N., Wu S., et al. . (2016). Correlation between ethanol resistance and characteristics of PQQ-dependent ADH in acetic acid bacteria. Eur. Food. Res. Technol. 242, 837–847. 10.1007/s00217-015-2589-5 - DOI
-
- Chinnawirotpisan P., Theeragool G., Limtong S., Toyama H., Adachi O. O., Matsushita K. (2003). Quinoprotein alcohol dehydrogenase is involved in catabolic acetate production, while NAD-dependent alcohol dehydrogenase in ethanol assimilation in Acetobacter pasteurianusSKU1108. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 96, 564–571. 10.1016/S1389-1723(04)70150-4 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

