Expression of hnRNPK & Claudin-4 in HCV-Induced Early HCC and Adjacent Liver Tissue
- PMID: 28932298
- PMCID: PMC5591587
- DOI: 10.3889/oamjms.2017.092
Expression of hnRNPK & Claudin-4 in HCV-Induced Early HCC and Adjacent Liver Tissue
Abstract
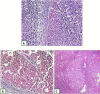
Background: HCC in Egypt usually occurs in HCV cirrhotic livers with poor prognosis due to late diagnosis. High hnRNPK & low Claudin-4 profiles indicate Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition (EMT), malignant transformation and high-grade tumours.
Aim: We studied the immunohistochemical expression of hnRNPK and Claudin-4 in HCV induced early HCC (eHCC) and adjacent liver tissue in Egyptian patients to improve eHCC detection in cirrhotic livers with better curative therapy options.
Method: We studied the immunohistochemical expression of hnRNPK and Claudin-4 in 100 Egyptian patients resection specimens of HCV induced early HCC (eHCC) and adjacent liver tissue, in order to improve eHCC detection in cirrhotic livers, thus improving their therapeutic options.
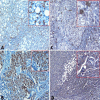
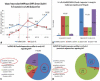
Results: Early HCC grade significantly directly correlated with nuclear hnRNPK/5HPFs count and inversely correlated with Claudin-4 expression %, with a converse correlation between hnRNPK and Claudin-4. Moreover in eHCC, combined hnRNPK ≥ 30/5HPFs & Claudin-4 ≥ 40% significantly distinguished low grade eHCC (G1) from high grade eHCC (G2&G3), with sensitivity 97% & specificity 69.7% for hnRNPK ≥ 30/5HPFs, and with sensitivity 70% & specificity 94.3% for Claudin-4 ≥ 40%. Moreover in the adjacent liver, both markers expressions significantly directly correlated with each other and with METAVIR fibrosis score but not with activity. Furthermore, 58% of eHCCs showed hnRNPK ≥ 30 Claudin-4 < 40% profile, indicating EMT type 3, compared to 26% with hnRNPK ≥ 30 Claudin-4 ≤ 10% profile in adjacent cirrhotic/ precirrhotic liver, with significant use of combined hnRNPK ≥ 30/5HPFs & Claudin 4 ≤ 10% as eHCC prediction cut offs in cirrhosis (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Combination of hnRNPK and Claudin-4 can indicate early HCC development in HCV cirrhotic livers using hnRNPK ≥ 30/5HPFs & Claudin-4 ≤ 10% cut offs. Also, combination of hnRNPK ≥ 30/5HPFs & Claudin-4 ≥ 40% can distinguish low grade eHCC (G1) from high grade eHCC (G2&G3).
Keywords: Claudin-4; EMT; Metavir; cirrhosis; eHCC; hnRNPK.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Dysplastic nodule of liver versus early hepatocellular carcinoma: a clinicopathologic and prognostic study].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2014 May;43(5):301-6. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 25030861 Chinese.
-
Serum Beta-2 Microglobulin: a Possible Marker for Disease Progression in Egyptian Patients with Chronic HCV Related Liver Diseases.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015;16(17):7825-9. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2015.16.17.7825. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015. PMID: 26625805
-
Role of circulating miR-182 and miR-150 as biomarkers for cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma post HCV infection in Egyptian patients.Virus Res. 2018 Aug 15;255:77-84. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2018.07.004. Epub 2018 Jul 9. Virus Res. 2018. PMID: 30003924
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Its Precursors in 103 HBV-Related Cirrhotic Explanted Livers: A Study from South Iran.Hepat Mon. 2016 Jul 20;16(8):e38584. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.38584. eCollection 2016 Aug. Hepat Mon. 2016. PMID: 27795725 Free PMC article.
-
Preneoplastic lesions in chronic hepatitis C.Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1995;25:171-8. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1995. PMID: 8875622 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum soluble Toll-like receptor 4 and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C virus patients.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2020;24(4):216-220. doi: 10.5114/wo.2020.102818. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2020. PMID: 33531868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- GLOBOCAN:2008 database (version 1.2) Available online: http://globocan.iarc.fr>;2008 .
-
- Ziada DH, El Sadany S, Soliman H, Abd-Elsalam S, Salama M, Hawash N, Selim A, Hamisa M, Elsabagh HM. Prevalence of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C patients in Mid Delta, Egypt:A single centre study. Journal of the Egyptian National Cancer Institute. 2016;28(4):257–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnci.2016.06.001 PMid:27378258. - PubMed
-
- Guo Y, Zhao J, Bi J, Wu Q, Wang X, Lai Q. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K (hnRNP K) is a tissue biomarker for detection of early Hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Journal of Hematology & Oncology. 2012;5:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-5-37 PMid:22760167 PMCid:PMC3425156. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Giannelli G, Bergamini E, Fransvea E, Sgarra C, Antonaci S. Laminin-5 with transforming growth factor-beta 1 induces epithelial to mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:1375–83. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2005.09.055 PMid:16285938. - PubMed
-
- Bataller R, Brenner DA. Liver fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115:209–18. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI24282 PMid:15690074 PMCid:PMC546435. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
