Cardiovascular involvement in celiac disease
- PMID: 28932354
- PMCID: PMC5583538
- DOI: 10.4330/wjc.v9.i8.652
Cardiovascular involvement in celiac disease
Abstract
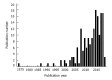
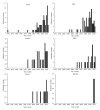
Celiac disease (CD) is an autoimmune response to ingestion of gluten protein, which is found in wheat, rye, and barley grains, and results in both small intestinal manifestations, including villous atrophy, as well as systemic manifestations. The main treatment for the disease is a gluten-free diet (GFD), which typically results in the restoration of the small intestinal villi, and restoration of other affected organ systems, to their normal functioning. In an increasing number of recently published studies, there has been great interest in the occurrence of alterations in the cardiovascular system in untreated CD. Herein, published studies in which CD and cardiovascular terms appear in the title of the study were reviewed. The publications were categorized into one of several types: (1) articles (including cohort and case-control studies); (2) reviews and meta-analyses; (3) case studies (one to three patient reports); (4) letters; (5) editorials; and (6) abstracts (used when no full-length work had been published). The studies were subdivided as either heart or vascular studies, and were further characterized by the particular condition that was evident in conjunction with CD. Publication information was determined using the Google Scholar search tool. For each publication, its type and year of publication were tabulated. Salient information from each article was then compiled. It was determined that there has been a sharp increase in the number of CD - cardiovascular studies since 2000. Most of the publications are either of the type "article" or "case study". The largest number of documents published concerned CD in conjunction with cardiomyopathy (33 studies), and there have also been substantial numbers of studies published on CD and thrombosis (27), cardiovascular risk (17), atherosclerosis (13), stroke (12), arterial function (11), and ischemic heart disease (11). Based on the published research, it can be concluded that many types of cardiovascular issues can occur in untreated CD patients, but that most tend to resolve on a GFD, often in conjunction with the healing of small intestinal villous atrophy. However, in some cases the alterations are irreversible, underscoring the need for CD screening and treatment when cardiovascular issues arise of unknown etiology.
Keywords: Cardiovascular; Celiac disease; Gluten; Heart; Vascular.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical utility of serologic testing for celiac disease in ontario: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010;10(21):1-111. Epub 2010 Dec 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2010. PMID: 23074399 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical utility of serologic testing for celiac disease in asymptomatic patients: an evidence-based analysis.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2011;11(3):1-63. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2011. PMID: 23074415 Free PMC article.
-
The potentials of probiotics on gluten hydrolysis; a review study.Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2020 Winter;13(Suppl1):S1-S7. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2020. PMID: 33584998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Celiac Disease and Sensitization to Wheat, Rye, and Barley: Should We Be Concerned?Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2021;182(5):440-446. doi: 10.1159/000512108. Epub 2020 Dec 15. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33321512
-
The role of celiac disease in severity of liver disorders and effect of a gluten free diet on diseases improvement.Hepat Mon. 2013 Oct 13;13(10):e11893. doi: 10.5812/hepatmon.11893. Hepat Mon. 2013. PMID: 24348636 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The incidence of heart attacks among young individuals in Mosul City.J Educ Health Promot. 2024 Jul 11;13:218. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_1266_23. eCollection 2024. J Educ Health Promot. 2024. PMID: 39297084 Free PMC article.
-
Atrioventricular Block in Celiac Disease: An Unusual Clinical Presentation in a Child. A Case-Based Review.Children (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;9(11):1627. doi: 10.3390/children9111627. Children (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36360355 Free PMC article.
-
Dilated cardiomyopathy associated with celiac disease: A case report.Clin Case Rep. 2021 Nov 12;9(11):e04990. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.4990. eCollection 2021 Nov. Clin Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34804528 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiomyopathy in Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Feb 12;13(4):1045. doi: 10.3390/jcm13041045. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38398359 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Celiac Male's Gluten-Free Diet Profile: Comparison to that of the Control Population and Celiac Women.Nutrients. 2018 Nov 8;10(11):1713. doi: 10.3390/nu10111713. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30413127 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lodha A, Haran M, Hollander G, Frankel R, Shani J. Celiac disease associated with dilated cardiomyopathy. South Med J. 2009;102:1052–1054. - PubMed
-
- Wang I, Hopper I. Celiac disease and drug absorption: implications for cardiovascular therapeutics. Cardiovasc Ther. 2014;32:253–256. - PubMed
-
- Ciaccio EJ, Bhagat G, Lewis SK, Green PH. Trends in celiac disease research. Comput Biol Med. 2015;65:369–378. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources