Research Associates Program: Expanding clinical research productivity with undergraduate students
- PMID: 28932396
- PMCID: PMC5598797
- DOI: 10.1177/2050312117730245
Research Associates Program: Expanding clinical research productivity with undergraduate students
Abstract
Objectives: Clinical research is often time-consuming and difficult to conduct in busy academic institutions. Previous studies have proposed methods to integrate undergraduate students as a means to increase research productivity. The authors aimed to describe the possibility to enhance emergency department research productivity at an academic emergency department in the United States, using undergraduate students in an Emergency Medicine Research Associates Program.
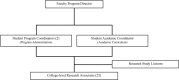
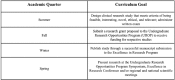
Methods: The authors described the Emergency Medicine Research Associates Program curriculum and its implementation. We also conducted a retrospective study at a university-based emergency department from January 2005 to December 2014 to demonstrate the benefit of having an established Emergency Medicine Research Associates Program. The primary outcomes were number of Emergency Medicine Research Associates Program-related studies, number of enrolled patients, extramural/intramural funding, abstract presentations, and peer-reviewed publications. The authors analyzed the data using descriptive statistics.
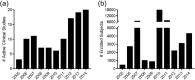
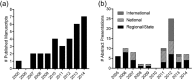
Results: Over the 10-year period, 110 Emergency Medicine Research Associates Program-assisted research studies were conducted, with research associates enrolling 46,219 patients. These studies yielded a total of 31 peer-reviewed publications and 77 abstract presentations (13 international, 27 national, 37 state/regional). The Emergency Medicine Research Associates Program-related studies were used as pilot studies to obtain US$1,751,036 in extramural grant funding and US$31,047 in intramural grant funding.
Conclusion: The implementation of Emergency Medicine Research Associates Program can enhance emergency department clinical research productivity, and the inclusion of supplemental academic programs enhanced the undergraduate students' research experience.
Keywords: Research associates; emergency department; funding; research productivity; research program; undergraduate.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
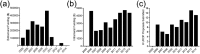
References
-
- Short A, Holdgate A, Ahern N, et al. Enhancing research interest and collaboration in the interdisciplinary context of emergency care. J Interprof Care 2009; 23: 156–168. - PubMed
-
- Gallagher EJ, Goldfrank L, Anderson GV, et al. Current status of academic emergency medicine within academic medicine in the United States. Acad Emerg Med 1994; 1: 41–46. - PubMed
-
- Lee CH, Shih CP, Chang YC, et al. The evolution of academic performance in emergency medicine journals: viewpoint from 2000 to 2009 journal citation reports. Acad Emerg Med 2011; 18: 898–904. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

