A clinician's guide to understanding resistance to thyroid hormone due to receptor mutations in the TRα and TRβ isoforms
- PMID: 28932413
- PMCID: PMC5603052
- DOI: 10.1186/s40842-017-0046-z
A clinician's guide to understanding resistance to thyroid hormone due to receptor mutations in the TRα and TRβ isoforms
Abstract
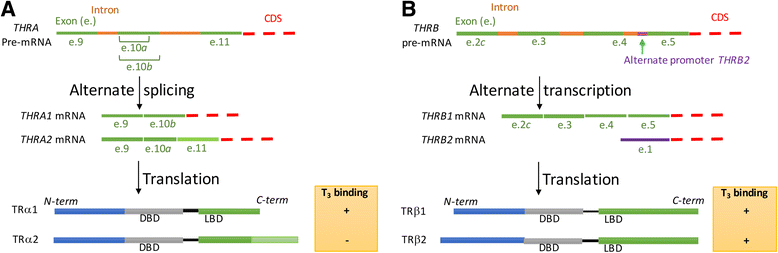
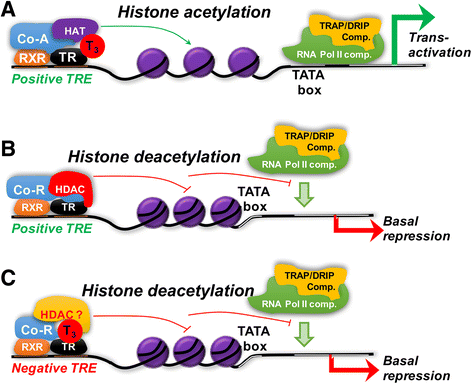
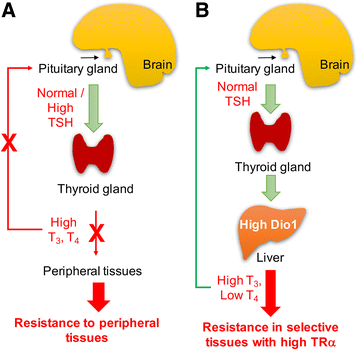
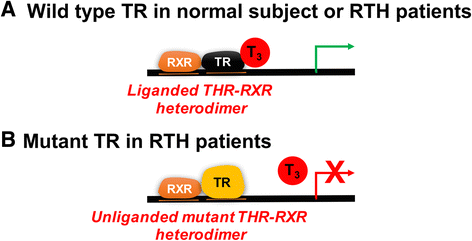
There are two genes that express the major thyroid hormone receptor isoforms. Mutations in both these genes have given rise to Resistance to Thyroid Hormone (RTH) syndromes (RTHβ, RTHα) that can have variable phenotypes for mutations of the same receptor isoform as well as between the two receptor isoforms. In general, the relative tissue-specific distribution of TRβ and TRα determine RTH in different tissues for each form of RTH. These differences highlight some of the isoform-specific roles of each TR isoform. The diagnosis of RTH is challenging for the clinician but should be considered whenever a patient presents with unexplained elevated serum free T4 (fT4) and unsuppressed TSH levels, as well as decreased serum free T4/T3 ratio. Here we provide a guide for the clinician to diagnose and treat both types of RTH.
Keywords: Dominant negative activity; Human mutation; Resistance to thyroid hormone; Thyroid hormone receptors; Thyroid stimulating hormone.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Manuscripts reporting studies involving human participants, human data or human tissue must: n/a.
Consent for publication
n/a
Competing interests
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Albright F, Burnett CH, Smith PH, Parson W. Pseudohypopara-thyroidism — an example of Seabright's bantam syndrome. Endocrinology. 1942;30:922.
-
- Ando S, Sarlis NJ, Oldfield EH, Yen PM. Somatic mutation of TRbeta can cause a defect in negative regulation of TSH in a TSH-secreting pituitary tumor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86:5572–5576. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

