A novel in silico framework to improve MHC-I epitopes and break the tolerance to melanoma
- PMID: 28932628
- PMCID: PMC5599093
- DOI: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1319028
A novel in silico framework to improve MHC-I epitopes and break the tolerance to melanoma
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Oncoimmunology. 2017 Oct 6;6(10):e1389146. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1389146. eCollection 2017. Oncoimmunology. 2017. PMID: 29123968 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Tolerance toward tumor antigens, which are shared by normal tissues, have often limited the efficacy of cancer vaccines. However, wild type epitopes can be tweaked to activate cross-reactive T-cell clones, resulting in antitumor activity. The design of these analogs (i.e., heteroclitic peptides) can be difficult and time-consuming since no automated in silico tools are available. Hereby we describe the development of an in silico framework to improve the selection of heteroclitic peptides. The Epitope Discovery and Improvement System (EDIS) was first validated by studying the model antigen SIINFEKL. Based on artificial neural network (ANN) predictions, we selected two mutant analogs that are characterized by an increased MHC-I binding affinity (SIINFAKL) or increased TCR stimulation (SIIWFEKL). Therapeutic vaccination using optimized peptides resulted in enhanced antitumor activity and against B16.OVA melanomas in vivo. The translational potential of the EDIS platform was further demonstrated by studying the melanoma-associated antigen tyrosinase related protein 2 (TRP2). Following therapeutic immunization with the EDIS-derived epitope SVYDFFAWL, a significant reduction in the growth of established B16.F10 tumors was observed, suggesting a break in the tolerance toward the wild type epitope. Finally, we tested a multi vaccine approach, demonstrating that combination of wild type and mutant epitopes targeting both TRP2 and OVA antigens increases the antitumor response. In conclusion, by taking advantage of available prediction servers and molecular dynamics simulations, we generated an innovative platform for studying the initial sequences and selecting lead candidates with improved immunological features. Taken together, EDIS is the first automated algorithm-driven platform to speed up the design of heteroclitic peptides that can be publicly queried online.
Keywords: Cancer vaccine; heteroclitic peptides; immunotherapy; in silico; prediction servers; tumor antigens.
Figures
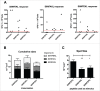
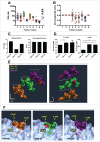
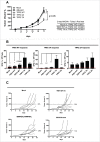
References
-
- Walter S, Weinschenk T, Stenzl A, Zdrojowy R, Pluzanska A, Szczylik C, Staehler M, Brugger W, Dietrich PY, Mendrzyk R et al.. Multipeptide immune response to cancer vaccine IMA901 after single-dose cyclophosphamide associates with longer patient survival. Nat Med 2012. August; 18(8):1254–61; PMID: 22842478; https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2883 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vacchelli E, Martins I, Eggermont A, Fridman WH, Galon J, Sautès-Fridman C, Tartour E, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L. Trial watch: peptide vaccines in cancer therapy. Oncoimmunology 2012; 1(9):1557-76; PMID: 23264902; https://doi.org/10.4161/onci.22428 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chianese-Bullock KA, Pressley J, Garbee C, Hibbitts S, Murphy C, Yamshchikov G, Petroni GR, Bissonette EA, Neese PY, Grosh WW et al.. MAGE-A1-, MAGE-A10-, and gp100-derived peptides are immunogenic when combined with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and montanide ISA-51 adjuvant and administered as part of a multipeptide vaccine for melanoma. J Immunol 2005; 174(5):3080-6; PMID: 15728523; https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.174.5.3080 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Menez-Jamet J, Gallou C, Rougeot A, Kosmatopoulos K. Optimized tumor cryptic peptides: the basis for universal neo-antigen-like tumor vaccines. Ann Transl Med 2016; 4(14):266; PMID: 27563653; https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2016.05.15 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hebeisen M, Allard M, Gannon PO, Schmidt J, Speiser DE, Rufer N. Identifying individual T Cell receptors of optimal avidity for tumor antigens. Front Immunol 2015; 6:582; PMID: 26635796; https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00582 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
