A practical approach for the validation and clinical implementation of a high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I assay across a North American city
- PMID: 28932796
- PMCID: PMC5597710
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plabm.2015.02.001
A practical approach for the validation and clinical implementation of a high-sensitivity cardiac troponin I assay across a North American city
Abstract
Objectives: Despite several publications on the analytical performance of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin (hs-cTn) assays, there has been little information on how laboratories should validate and implement these assays into clinical service. Our study provides a practical approach for the validation and implementation of a hs-cTn assay across a large North American City.
Design and methods: Validation for the Abbott ARCHITECT hs-cTnI assay (across 5 analyzers) consisted of verification of limit of blank (LoB), precision (i.e., coefficient of variation; CV) testing at the reported limit of detection (LoD) and within and outside the 99th percentile, linearity testing, cTnI versus hs-cTnI patient comparison within and between analyzers (Passing and Bablok and non-parametric analyses). Education, clinical communications, and memorandums were issued in advance to inform all staff across the city as well as a selected reminder the day before live-date to important users. All hospitals switched to the hs-cTnI assay concurrently (the contemporary cTnI assay removed) with laboratory staff instructed to repeat samples previously measured with the contemporary cTnI assay with the hs-cTnI assay only by physician request.
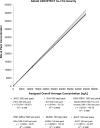
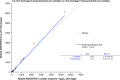
Results: Across the 5 analyzers and 6 reagent packs the overall LoB was 0.6 ng/L (n=60) with a CV of 33% at an overall mean of 1.2 ng/L (n=60; reported LoD=1.0 ng/L), with linearity demonstrated from 45,005 ng/L to 1.1 ng/L. Precision testing with a normal patient-pool QC material (mean range across 5 analyzers was 3.9-4.4 ng/L) yielded a range of CVs from 7% to 10% (within-run) and CVs from 7% to 18% (between-run) with the high patient-pool QC material (mean range across 5 analyzers was 29.6-36.3 ng/L) yielding a range of CVs from 2% to 5% (within-run) and CVs from 4% to 8% (between-run). There was agreement between hs-cTnI versus cTnI with the patient samples (slope ranges: 0.89-1.03; intercept ranges: 1.9-3.8 ng/L), however, the median CV on patient samples <100 ng/L across the analyzers was 5.6% for hs-cTnI versus 18.7% for the contemporary assay (p<0.001). Following the switch to hs-cTnI testing, no requests for repeat measurements were received.
Conclusions: Validation and implementation of hs-cTnI testing across multiple sites requires collaboration within the laboratories and between hospital laboratories and clinical staff.
Keywords: High-sensitivity cardiac troponin; Implementation; Multicenter; Quality; Validation.
Figures

References
-
- Kavsak P.A. Early standardization of high sensitivity troponin T reporting – a lost opportunity. Clin Biochem. 2011;44:758–759. - PubMed
-
- High-sensitivity cardiac troponin for the rapid diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome in the emergency department: a clinical and cost-effectiveness evaluation [Internet]. Source: Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; March 2013. 〈http://www.cadth.ca/en/products/optimal-use/ high-sensitivity-troponin〉. - PubMed
-
- Kavsak P.A., Jaffe A.S., Hickman P.E., Mills N.L., Humphries K.H., McRae A. Canadian Institutes of Health Research dissemination grant on high-sensitivity cardiac troponin. Clin Biochem. 2014;47:155–157. - PubMed
-
- Kavsak P.A., Allen L.C., Apple F.S., Booth R.A., Chan P.C., Delvin E. Cardiac troponin testing in the acute care setting: ordering, reporting, and high sensitivity assays—an update from the Canadian society of clinical chemists (CSCC) Clin Biochem. 2011;44:1273–1277. - PubMed
-
- Apple F.S., Collinson P.O., IFCC Task Force on Clinical Applications of Cardiac Biomarkers Analytical characteristics of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin assays. Clin Chem. 2012;58:54–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

