A Quorum-Sensing System That Regulates Streptococcus pneumoniae Biofilm Formation and Surface Polysaccharide Production
- PMID: 28932816
- PMCID: PMC5597970
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00324-17
A Quorum-Sensing System That Regulates Streptococcus pneumoniae Biofilm Formation and Surface Polysaccharide Production
Abstract
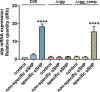
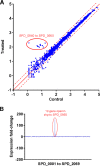
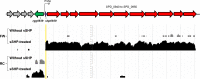
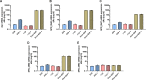
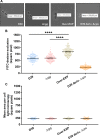
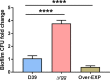
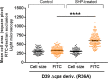
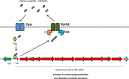
Despite vaccines, Streptococcus pneumoniae kills more than a million people yearly. Thus, understanding how pneumococci transition from commensals to pathogens is particularly relevant. Quorum sensing regulates collective behaviors and thus represents a potential driver of commensal-to-pathogen transitions. Rgg/small hydrophobic peptide (SHP) quorum-sensing systems are widespread in streptococci, yet they remain largely uncharacterized in S. pneumoniae. Using directional transcriptome sequencing, we show that the S. pneumoniae D39 Rgg0939/SHP system induces the transcription of a single gene cluster including shp and capsule gene homologs. Capsule size measurements determined by fluorescein isothiocyanate-dextran exclusion allowed assignment of the system to the regulation of surface polysaccharide expression. We found that the SHP pheromone induced exopolysaccharide expression in R36A, an unencapsulated derivative of D39. In the encapsulated parent strain, overexpression of the Rgg system resulted in a mutant with increased capsule size. In line with previous studies showing that capsule expression is inversely associated with biofilm formation, we found that biofilm formed on lung epithelial cells was decreased in the overexpression strain and increased in an rgg deletion mutant. Although no significant differences were observed between D39 and the rgg deletion mutant in a mouse model of lung infection, in competitive assays, overexpression reduced fitness. This is the first study to reveal a quorum-sensing system in streptococci that regulates exopolysaccharide synthesis from a site distinct from the original capsule locus. IMPORTANCE Quorum sensing regulates bacterial social behaviors by production, secretion, and sensing of pheromones. In this study, we characterized a new quorum-sensing system of the Rgg/SHP class in S. pneumoniae D39. The system was found to directly induce the expression of a single gene cluster comprising the gene for the SHP pheromone and genes with putative functions in capsule synthesis. Capsule size, as measured by dextran exclusion, was increased by SHP exposure in R36A, an unencapsulated derivative of D39. In the encapsulated parent strain, overexpression of the gene cluster increased capsule size, supporting the role of Rgg/SHP in the synthesis of surface polysaccharides. Further, we found that biofilm formation on epithelial cells was reduced by overexpression of the system and increased in a mutant with an rgg deletion. Placing surface polysaccharide expression under quorum-sensing regulation may enable S. pneumoniae to tune interactions with the host and other bacteria in accordance with environmental and cell density conditions.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; biofilms; cell signaling; mutagenesis; natural transformation systems; polysaccharides; quorum sensing; rgg; shp; transcriptional regulation.
Figures
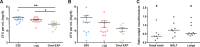
References
-
- O’Brien KL, Wolfson LJ, Watt JP, Henkle E, Deloria-Knoll M, McCall N, Lee E, Mulholland K, Levine OS, Cherian T, Hib and Pneumococcal Global Burden of Disease Study Team . 2009. Burden of disease caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae in children younger than 5 years: global estimates. Lancet 374:893–902. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61204-6. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hamaluba M, Kandasamy R, Ndimah S, Morton R, Caccamo M, Robinson H, Kelly S, Field A, Norman L, Plested E, Thompson BA, Zafar A, Kerridge SA, Lazarus R, John T, Holmes J, Fenlon SN, Gould KA, Waight P, Hinds J, Crook D, Snape MD, Pollard AJ. 2015. A cross-sectional observational study of pneumococcal carriage in children, their parents, and older adults following the introduction of the 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine. Medicine 94:e335. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000335. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Le Polain de Waroux O, Flasche S, Prieto-Merino D, Edmunds WJ. 2014. Age-dependent prevalence of nasopharyngeal carriage of Streptococcus pneumoniae before conjugate vaccine introduction: a prediction model based on a meta-analysis. PLoS One 9:e86136. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086136. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

