Required hydrophobicity of fluorescent reporters for phosphatidylinositol family of lipid enzymes
- PMID: 28932942
- PMCID: PMC5671358
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-017-0633-y
Required hydrophobicity of fluorescent reporters for phosphatidylinositol family of lipid enzymes
Abstract
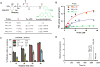
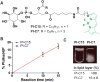
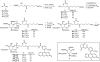
The phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns) family of lipids plays important roles in cell differentiation, proliferation, and migration. Abnormal expression, mutation, or regulation of their metabolic enzymes has been associated with various human diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and bipolar disorder. Recently, fluorescent derivatives have increasingly been used as chemical probes to monitor either lipid localization or enzymatic activity. However, the requirements of a good probe have not been well defined, particularly modifications on the diacylglycerol side chain partly due to challenges in generating PtdIns lipids. We have synthesized a series of fluorescent PtdIns(4,5)P2 (PIP2) and PtdIns (PI) derivatives with various lengths of side chains and tested their capacity as substrates for PI3KIα and PI4KIIα, respectively. Both capillary electrophoresis and thin-layer chromatography were used to analyze enzymatic reactions. For both enzymes, the fluorescent probe with a longer side chain functions as a better substrate than that with a shorter chain and works well in the presence of the endogenous lipid, highlighting the importance of hydrophobicity of side chains in fluorescent phosphoinositide reporters. This comparison is consistent with their interactions with lipid vesicles, suggesting that the binding of a fluorescent lipid with liposome serves as a standard for assessing its utility as a chemical probe for the corresponding endogenous lipid. These findings are likely applicable to other lipid enzymes where the catalysis takes place at the lipid-water interface.
Keywords: Chemical cytometry; Fluorescent reporter; Lipid enzyme; Phosphatidylinositol.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

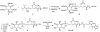
Similar articles
-
Lipid products of phosphoinositide 3-kinase bind human profilin with high affinity.Biochemistry. 1996 Nov 5;35(44):14027-34. doi: 10.1021/bi961878z. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8909300
-
Synthesis of hybrid lipid probes: derivatives of phosphatidylethanolamine-extended phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (Pea-PIP(2)).J Org Chem. 2002 Aug 9;67(16):5454-60. doi: 10.1021/jo011185a. J Org Chem. 2002. PMID: 12153242
-
Kinetic analysis of PI3K reactions with fluorescent PIP2 derivatives.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011 Oct;401(6):1881-8. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5257-z. Epub 2011 Jul 26. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011. PMID: 21789487 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphatidylinositol signalling reactions.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1998 Apr;9(2):153-60. doi: 10.1006/scdb.1997.0220. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 1998. PMID: 9599410 Review.
-
Following the trail of lipids: Signals initiated by PI3K function at multiple cellular membranes.Sci Signal. 2016 May 17;9(428):re4. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aad7885. Sci Signal. 2016. PMID: 27188443 Review.
Cited by
-
2-O-Acetyl-3,4,5,6-tetra-O-benzyl-d-myo-inosityl diphenylphosphate: A new useful intermediate to inositol phosphate and phospholipids.Chirality. 2022 Aug;34(8):1038-1043. doi: 10.1002/chir.23457. Epub 2022 May 9. Chirality. 2022. PMID: 35531652 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

