Lung cancer screening with MRI: results of the first screening round
- PMID: 28932985
- PMCID: PMC11813265
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-017-2521-4
Lung cancer screening with MRI: results of the first screening round
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the suitability of MRI for lung cancer screening in a high-risk population.
Materials and methods: A 5-year lung cancer screening program comparing MRI and low-dose CT (LDCT) in a high-risk population was initiated. 224 subjects were examined with MRI and LDCT. Acquired MRI sequences were T2w MultiVane XD, balanced steady-state-free precession, 3D T1w GRE, and DWI with a maximum in-room-time of 20 min. Categorization and management of nodules were based on Lung-RADS. MRI findings were correlated with LDCT as a reference. Here, we report on the first screening round.
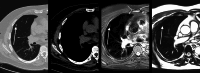
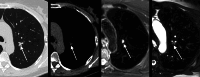
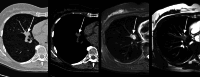
Results: MRI accurately detected 61 of 88 nodules 4-5 mm, 20 of 21 nodules 6-7 mm, 12 of 12 nodules 8-14 mm, 4 of 4 nodules ≥ 15 mm (solid nodules), and 8 of 11 subsolid nodules. Sensitivity/specificity of MRI for nodule detection was 69.3/96.4% for 4-5 mm, 95.2/99.6% for 6-7 mm, 100/99.6% for 8-14 mm, 100/100% for ≥ 15 mm (solid nodules), and 72.7/99.2% for subsolid nodules. The early recall rate was 13.8% for MRI and 12.5% for LDCT. Following Lung-RADS recommendations and based on interdisciplinary consensus, histology was obtained in eight subjects. The biopsy rate was 3.6% for MRI and 3.4% for LDCT. In all of these eight cases, the nodules were carcinomas, and all of them were accurately detected by MRI.
Conclusion: The results of the first screening round suggest that MRI is suitable for lung cancer screening with an excellent sensitivity and specificity for nodules ≥ 6 mm.
Keywords: Lung cancer; MRI; Screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
"Commentary on: Lung cancer screening with MRI: results of the first screening round"-Michael Meier-Schroers et al.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018 Jul;144(7):1395-1396. doi: 10.1007/s00432-018-2655-z. Epub 2018 May 10. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29748712 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- American College of Radiology (2017) Lung CT screening reporting and data system (Lung-RADS). Available at: http://www.acr.org/Quality-Safety/Resources/LungRADS. Accessed 31 March 2017
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

