Mitochondrial Dynamics in Mitochondrial Diseases
- PMID: 28933354
- PMCID: PMC5456341
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases5010001
Mitochondrial Dynamics in Mitochondrial Diseases
Abstract
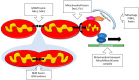
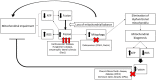
Mitochondria are very versatile organelles in continuous fusion and fission processes in response to various cellular signals. Mitochondrial dynamics, including mitochondrial fission/fusion, movements and turnover, are essential for the mitochondrial network quality control. Alterations in mitochondrial dynamics can cause neuropathies such as Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease in which mitochondrial fusion and transport are impaired, or dominant optic atrophy which is caused by a reduced mitochondrial fusion. On the other hand, mitochondrial dysfunction in primary mitochondrial diseases promotes reactive oxygen species production that impairs its own function and dynamics, causing a continuous vicious cycle that aggravates the pathological phenotype. Mitochondrial dynamics provides a new way to understand the pathophysiology of mitochondrial disorders and other diseases related to mitochondria dysfunction such as diabetes, heart failure, or Hungtinton's disease. The knowledge about mitochondrial dynamics also offers new therapeutics targets in mitochondrial diseases.
Keywords: mitochondrial disease; mitochondrial dynamics; mitochondrial fusion; mitocondrial fission; mitophagy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of mitochondrial network dynamics in the pathogenesis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009;652:129-37. doi: 10.1007/978-90-481-2813-6_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2009. PMID: 20225023 Review.
-
Mitochondrial dynamics--fusion, fission, movement, and mitophagy--in neurodegenerative diseases.Hum Mol Genet. 2009 Oct 15;18(R2):R169-76. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddp326. Hum Mol Genet. 2009. PMID: 19808793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial fusion/fission dynamics in neurodegeneration and neuronal plasticity.Neurobiol Dis. 2016 Jun;90:3-19. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.10.011. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Neurobiol Dis. 2016. PMID: 26494254 Review.
-
Mitochondrial trafficking and morphology in neuronal injury.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Jan;1802(1):143-50. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.09.005. Epub 2009 Sep 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19747973 Review.
-
Mitochondrial dynamics and inherited peripheral nerve diseases.Neurosci Lett. 2015 Jun 2;596:66-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2015.04.001. Epub 2015 Apr 3. Neurosci Lett. 2015. PMID: 25847151 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Liraglutide in Lithium-Pilocarpine-Induced Temporal Lobe Epilepsy Model in Rats: Impact on Inflammation, Mitochondrial Function, and Behavior.Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 27;12(10):2205. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102205. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457518 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated metabolism and epigenetic modifications in the macrophages of mice in responses to cold stress.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022 Jun 15;23(6):461-480. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2101091. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2022. PMID: 35686526 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Dynamics in Basal and Stressful Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Feb 13;19(2):564. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020564. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29438347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LATS2 Deletion Attenuates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Promoting Mitochondrial Biogenesis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Aug 17;2021:1058872. doi: 10.1155/2021/1058872. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. Retraction in: Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2023 Jan 23;2023:9763942. doi: 10.1155/2023/9763942. PMID: 34457109 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Mitostasis, Calcium and Free Radicals in Health, Aging and Neurodegeneration.Biomolecules. 2021 Jul 10;11(7):1012. doi: 10.3390/biom11071012. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34356637 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hofmann S., Bauer M.F. Mitochondrial Disorders. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2001.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

