RegentK and Physiotherapy-Electrodermal Mapping
- PMID: 28933375
- PMCID: PMC5532978
- DOI: 10.3390/medicines1010022
RegentK and Physiotherapy-Electrodermal Mapping
Abstract
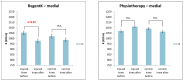
Background: Within this study, a new system which measures and analyzes electrical skin impedance in 48 channels within a 2.5 × 3.5 cm matrix is used in rehabilitation medicine for the first time. Methods: Electrodermal activity was measured in 20 patients before and after two different non-surgical treatments of a completely ruptured anterior cruciate ligament. The first treatment, RegentK, was developed by Mohamed Khalifa, the second is a standard physiotherapy. Results: The patients in the two groups were age-matched, and all demographic data showed no significant differences. It was interesting that electrodermal activity was significantly decreased only after RegentK. Conclusion: We conclude that not only local effects of pressure application are responsible for these results, rather as yet unknown neurovegetative mechanisms have to be taken into consideration.
Keywords: Khalifa therapy; RegentK; anterior cruciate ligament; electrical skin resistance; electrodermal mapping; physiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Dekker R., Kingma J., Groothoff J.W., Eisma W.H., Ten Duis H.J. Measurement of severity of sports injuries: An epidemiological study. Clin. Rehabil. 2000;14:651–656. - PubMed
-
- Dekker R., Groothoff J.W., van der Sluis C.K., Eisma W.H., Ten Duis H.J. Long-term disabilities and handicaps following sports injuries: Outcome after outpatient treatment. Disabil. Rehabil. 2003;25:1153–1157. - PubMed
-
- Majewski M., Susanne H., Klaus S. Epidemiology of athletic knee injuries: A 10-year study. Knee. 2006;13:184–188. - PubMed
-
- Ofner M., Kastner A., Wallenböck E., Pehn R., Schneider F., Gröll R., Szolar D., Walach H., Litscher G., Sandner-Kiesling A. Manual Khalifa therapy improves functional and morphological outcome of patients with anterior cruciate ligament rupture in the knee: A randomized controlled trial. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2014;2014:462840. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

