Phosphoproteome-based kinase activity profiling reveals the critical role of MAP2K2 and PLK1 in neuronal autophagy
- PMID: 28933595
- PMCID: PMC5788482
- DOI: 10.1080/15548627.2017.1371393
Phosphoproteome-based kinase activity profiling reveals the critical role of MAP2K2 and PLK1 in neuronal autophagy
Abstract
Recent studies have demonstrated that dysregulation of macroautophagy/autophagy may play a central role in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders, and the induction of autophagy protects against the toxic insults of aggregate-prone proteins by enhancing their clearance. Thus, autophagy has become a promising therapeutic target against neurodegenerative diseases. In this study, quantitative phosphoproteomic profiling together with a computational analysis was performed to delineate the phosphorylation signaling networks regulated by 2 natural neuroprotective autophagy enhancers, corynoxine (Cory) and corynoxine B (Cory B). To identify key regulators, namely, protein kinases, we developed a novel network-based algorithm of in silico Kinome Activity Profiling (iKAP) to computationally infer potentially important protein kinases from phosphorylation networks. Using this algorithm, we observed that Cory or Cory B potentially regulated several kinases. We predicted and validated that Cory, but not Cory B, downregulated a well-documented autophagy kinase, RPS6KB1/p70S6K (ribosomal protein S6 kinase, polypeptide 1). We also discovered 2 kinases, MAP2K2/MEK2 (mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2) and PLK1 (polo-like kinase 1), to be potentially upregulated by Cory, whereas the siRNA-mediated knockdown of Map2k2 and Plk1 significantly inhibited Cory-induced autophagy. Furthermore, Cory promoted the clearance of Alzheimer disease-associated APP (amyloid β [A4] precursor protein) and Parkinson disease-associated SNCA/α-synuclein (synuclein, α) by enhancing autophagy, and these effects were dramatically diminished by the inhibition of the kinase activities of MAP2K2 and PLK1. As a whole, our study not only developed a powerful method for the identification of important regulators from the phosphoproteomic data but also identified the important role of MAP2K2 and PLK1 in neuronal autophagy.
Keywords: autophagy; corynoxine; kinase activity; phosphoproteome; phosphorylation; protein kinase.
Figures

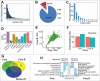



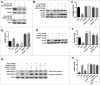

Comment in
-
Identification of neuronal autophagy regulators: Combined use of iKAP and THANATOS.Mov Disord. 2018 Apr;33(4):580-581. doi: 10.1002/mds.27354. Mov Disord. 2018. PMID: 29624753 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Corynoxine, a natural autophagy enhancer, promotes the clearance of alpha-synuclein via Akt/mTOR pathway.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014 Jun;9(3):380-7. doi: 10.1007/s11481-014-9528-2. Epub 2014 Feb 13. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24522518
-
Corynoxine B ameliorates HMGB1-dependent autophagy dysfunction during manganese exposure in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells.Food Chem Toxicol. 2019 Feb;124:336-348. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.12.027. Epub 2018 Dec 19. Food Chem Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30578841
-
Corynoxine promotes TFEB/TFE3-mediated autophagy and alleviates Aβ pathology in Alzheimer's disease models.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 May;45(5):900-913. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01197-1. Epub 2024 Jan 15. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 38225393 Free PMC article.
-
α-Synuclein phosphorylation as a therapeutic target in Parkinson's disease.Rev Neurosci. 2012 Mar 21;23(2):191-8. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2011-0067. Rev Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22499677 Review.
-
Autophagy in Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Hunter for Aggregates.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 10;21(9):3369. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093369. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32397599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A mode of action protein based approach that characterizes the relationships among most major diseases.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 20;15(1):9668. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93377-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40113859 Free PMC article.
-
A Global Phosphorylation Atlas of Proteins Within Pathological Site of Rotator Cuff Tendinopathy.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Feb 15;8:787008. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.787008. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35242811 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Uncaria rhynchophylla in the Potential Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease by Integrating Virtual Screening and In Vitro Validation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 22;24(20):15457. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015457. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895137 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging proteomic approaches to identify the underlying pathophysiology of neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders.Mol Autism. 2020 Apr 21;11(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s13229-020-00334-5. Mol Autism. 2020. PMID: 32317014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel protein kinase C phosphorylated kinase inhibitor-matrine suppresses replication of hepatitis B virus via modulating the mitogen-activated protein kinase signal.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):2851-2865. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2024957. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35037840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yang DS, Stavrides P, Mohan PS, Kaushik S, Kumar A, Ohno M, Schmidt SD, Wesson D, Bandyopadhyay U, Jiang Y, et al.. Reversal of autophagy dysfunction in the TgCRND8 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease ameliorates amyloid pathologies and memory deficits. Brain. 2011;134:258–77. doi:10.1093/brain/awq341. PMID:21186265. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
