Regulation of proliferation in developing human tooth germs by MSX homeodomain proteins and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p19INK4d
- PMID: 28933666
- PMCID: PMC5669213
- DOI: 10.1080/15476278.2017.1358337
Regulation of proliferation in developing human tooth germs by MSX homeodomain proteins and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p19INK4d
Abstract
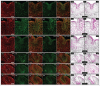
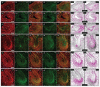
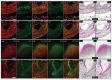
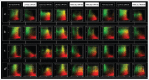
Before the secretion of hard dental tissues, tooth germs undergo several distinctive stages of development (dental lamina, bud, cap and bell). Every stage is characterized by specific proliferation patterns, which is regulated by various morphogens, growth factors and homeodomain proteins. The role of MSX homeodomain proteins in odontogenesis is rather complex. Expression domains of genes encoding for murine Msx1/2 during development are observed in tissues containing highly proliferative progenitor cells. Arrest of tooth development in Msx knockout mice can be attributed to impaired proliferation of progenitor cells. In Msx1 knockout mice, these progenitor cells start to differentiate prematurely as they strongly express cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p19INK4d. p19INK4d induces terminal differentiation of cells by blocking the cell cycle in mitogen-responsive G1 phase. Direct suppression of p19INK4d by Msx1 protein is, therefore, important for maintaining proliferation of progenitor cells at levels required for the normal progression of tooth development. In this study, we examined the expression patterns of MSX1, MSX2 and p19INK4d in human incisor tooth germs during the bud, cap and early bell stages of development. The distribution of expression domains of p19INK4d throughout the investigated period indicates that p19INK4d plays active role during human tooth development. Furthermore, comparison of expression domains of p19INK4d with those of MSX1, MSX2 and proliferation markers Ki67, Cyclin A2 and pRb, indicates that MSX-mediated regulation of proliferation in human tooth germs might not be executed by the mechanism similar to one described in developing tooth germs of wild-type mouse.
Keywords: MSX1; MSX2; cell cycle; development; human tooth germ; p19INK4d; proliferation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cranial neural crest-derived mesenchymal proliferation is regulated by Msx1-mediated p19(INK4d) expression during odontogenesis.Dev Biol. 2003 Sep 1;261(1):183-96. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(03)00300-2. Dev Biol. 2003. PMID: 12941628
-
The expression pattern of the cell cycle inhibitor p19(INK4d) by progenitor cells of the rat embryonic telencephalon and neonatal anterior subventricular zone.J Neurosci. 2001 May 1;21(9):3092-103. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.21-09-03092.2001. J Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11312294 Free PMC article.
-
Homeobox protein MSX-1 inhibits expression of bone morphogenetic protein 2, bone morphogenetic protein 4, and lymphoid enhancer-binding factor 1 via Wnt/β-catenin signaling to prevent differentiation of dental mesenchymal cells during the late bell stage.Eur J Oral Sci. 2018 Feb;126(1):1-12. doi: 10.1111/eos.12390. Epub 2017 Nov 17. Eur J Oral Sci. 2018. PMID: 29148101
-
Intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of the proliferation and differentiation of cells in the rodent rostral migratory stream.J Neurosci Res. 2002 Sep 15;69(6):795-802. doi: 10.1002/jnr.10336. J Neurosci Res. 2002. PMID: 12205673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p19INK4D and cell death.Cell Cycle. 2006 Mar;5(6):596-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.5.6.2585. Epub 2006 Mar 15. Cell Cycle. 2006. PMID: 16582618 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of Cell Cycle Markers and Proliferation Factors during Human Eye Embryogenesis and Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 20;23(16):9421. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169421. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012688 Free PMC article.
-
Syndecans and Enzymes for Heparan Sulfate Biosynthesis and Modification Differentially Correlate With Presence of Inflammatory Infiltrate in Periodontitis.Front Physiol. 2019 Sep 25;10:1248. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01248. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31611818 Free PMC article.
-
Heparan Sulfate Glycosaminoglycan Is Predicted to Stabilize Inflammatory Infiltrate Formation and RANKL/OPG Ratio in Severe Periodontitis in Humans.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Oct 18;9(10):566. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9100566. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290535 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical Localization of Endothelin- 1 and Endothelin A Receptor in Human Primary Tooth Enamel Organ.J Dent (Shiraz). 2023 Sep;24(3):328-334. doi: 10.30476/dentjods.2022.95201.1845. J Dent (Shiraz). 2023. PMID: 37727358 Free PMC article.
-
Spatio-Temporal Expression Pattern of Ki-67, pRB, MMP-9 and Bax in Human Secondary Palate Development.Life (Basel). 2021 Feb 20;11(2):164. doi: 10.3390/life11020164. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672637 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
