A Novel Fluoroimmunoassay for Detecting Ruscogenin with Monoclonal Antibodies Conjugated with CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots
- PMID: 28933731
- PMCID: PMC6152124
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22081250
A Novel Fluoroimmunoassay for Detecting Ruscogenin with Monoclonal Antibodies Conjugated with CdSe/ZnS Quantum Dots
Abstract
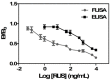
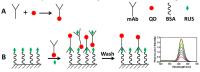
Ruscogenin (RUS) is a steroidal sapogenin found in Ruscus aculeatus and Ophiopogon japonicus with several pharmacological activities. In the work reported herein, a novel method termed competitive fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay (cFLISA) based on monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) coupled with quantum dots (QDs) was developed for the quick and sensitive determination of RUS in biological samples. The mAbs against RUS were conjugated with CdSe/ZnS QDs by the crossing-linking reagents and an indirect cFLISA method was developed. There was a good linear relationship between inhibition efficiency and logarithm concentration of RUS which was varied from 0.1 to 1000 ng/mL. The IC50 and limit of detection (LOD) were 9.59 ng/mL and 0.016 ng/mL respectively, which much lower than the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. The recoveries in plasma and tissues were ranged from 82.3% to 107.0% and the intra- and inter-day precision values were below 15%. The developed cFLISA has been successfully applied to the measurement of the concentrations of RUS in biological samples of rats, and showed great potential for the tissue distribution study of RUS. The cFLISA method may provide a valuable tool for the analysis of small molecules in biological samples and such an approach could be applied to other natural products.
Keywords: fluorescent immunosorbent assay; monoclonal antibody; quantum dots; ruscogenin; tissue distribution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Highly sensitive and accurate detection of C-reactive protein by CdSe/ZnS quantum dot-based fluorescence-linked immunosorbent assay.J Nanobiotechnology. 2017 May 2;15(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12951-017-0267-4. J Nanobiotechnology. 2017. PMID: 28464873 Free PMC article.
-
Monoclonal antibody-quantum dots CdTe conjugate-based fluoroimmunoassay for the determination of aflatoxin B1 in peanuts.Food Chem. 2014 Mar 1;146:314-9. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.048. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Food Chem. 2014. PMID: 24176348
-
Novel fluoroimmunoassays for detecting ochratoxin A using CdTe quantum dots.J Biophotonics. 2017 May;10(5):657-663. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201600005. Epub 2016 May 31. J Biophotonics. 2017. PMID: 27243787
-
Stability and fluorescence quantum yield of CdSe-ZnS quantum dots--influence of the thickness of the ZnS shell.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008;1130:235-41. doi: 10.1196/annals.1430.021. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2008. PMID: 18596353 Review.
-
[Functional analysis of bioactive natural compounds using monoclonal antibodies against natural compounds].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2014;134(10):1061-7. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.14-00178. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2014. PMID: 25274217 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
A highly sensitive fluorescent immunosensor for sensitive detection of nuclear matrix protein 22 as biomarker for early stage diagnosis of bladder cancer.RSC Adv. 2020 Aug 4;10(48):28865-28871. doi: 10.1039/d0ra06191c. eCollection 2020 Aug 3. RSC Adv. 2020. PMID: 35520044 Free PMC article.
-
Tetracycline-grafted mPEG-PLGA micelles for bone-targeting and osteoporotic improvement.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 14;13:993095. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.993095. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36188546 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cao G., Jiang N., Hu Y., Zhang Y., Wang G., Yin M., Ma X., Zhou K., Qi J., Yu B., et al. Ruscogenin Attenuates Cerebral Ischemia-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction by Suppressing TXNIP/NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and the MAPK Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016;17:E1418. doi: 10.3390/ijms17091418. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liu H., Zheng Y.F., Li C.Y., Zheng Y.Y., Wang D.Q., Wu Z., Huang L., Wang Y.G., Li P.B., Peng W., et al. Discovery of Anti-inflammatory Ingredients in Chinese Herbal Formula Kouyanqing Granule based on Relevance Analysis between Chemical Characters and Biological Effects. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:18080. doi: 10.1038/srep18080. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yu B.-Y. Exploration on the Modern Research Methodology of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Based on the Systemic Research of Radix Ophiopogonis. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2007;5:10–14.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

