Integrity of Cerebellar Fastigial Nucleus Intrinsic Neurons Is Critical for the Global Ischemic Preconditioning
- PMID: 28934119
- PMCID: PMC5664048
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci7100121
Integrity of Cerebellar Fastigial Nucleus Intrinsic Neurons Is Critical for the Global Ischemic Preconditioning
Abstract
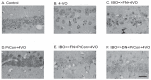
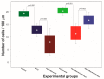
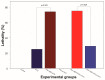
Excitation of intrinsic neurons of cerebellar fastigial nucleus (FN) renders brain tolerant to local and global ischemia. This effect reaches a maximum 72 h after the stimulation and lasts over 10 days. Comparable neuroprotection is observed following sublethal global brain ischemia, a phenomenon known as preconditioning. We hypothesized that FN may participate in the mechanisms of ischemic preconditioning as a part of the intrinsic neuroprotective mechanism. To explore potential significance of FN neurons in brain ischemic tolerance we lesioned intrinsic FN neurons with excitotoxin ibotenic acid five days before exposure to 20 min four-vessel occlusion (4-VO) global ischemia while analyzing neuronal damage in Cornu Ammoni area 1 (CA1) hippocampal area one week later. In FN-lesioned animals, loss of CA1 cells was higher by 22% compared to control (phosphate buffered saline (PBS)-injected) animals. Moreover, lesion of FN neurons increased morbidity following global ischemia by 50%. Ablation of FN neurons also reversed salvaging effects of five-minute ischemic preconditioning on CA1 neurons and morbidity, while ablation of cerebellar dentate nucleus neurons did not change effect of ischemic preconditioning. We conclude that FN is an important part of intrinsic neuroprotective system, which participates in ischemic preconditioning and may participate in naturally occurring neuroprotection, such as "diving response".
Keywords: cerebral ischemia; fastigial nucleus; hypoxic-ischemic brain injury; ischemic preconditioning; neuroprotection; pathophysiology; physiology; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

