Topical Nano and Microemulsions for Skin Delivery
- PMID: 28934172
- PMCID: PMC5750643
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics9040037
Topical Nano and Microemulsions for Skin Delivery
Abstract
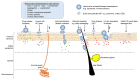
Nanosystems such as microemulsions (ME) and nanoemulsions (NE) offer considerable opportunities for targeted drug delivery to and via the skin. ME and NE are stable colloidal systems composed of oil and water, stabilised by a mixture of surfactants and cosurfactants, that have received particular interest as topical skin delivery systems. There is considerable scope to manipulate the formulation components and characteristics to achieve optimal bioavailability and minimal skin irritancy. This includes the incorporation of established chemical penetration enhancers to fluidize the stratum corneum lipid bilayers, thus reducing the primary skin barrier and increasing permeation. This review discusses nanosystems with utility in skin delivery and focuses on the composition and characterization of ME and NE for topical and transdermal delivery. The mechanism of skin delivery across the stratum corneum and via hair follicles is reviewed with particular focus on the influence of formulation.
Keywords: microemulsion; nanoemulsion; nanosystem; penetration enhancer; skin penetration; transdermal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Scheuplein R.J., Blank I.H. Permeability of the skin. Physiol. Rev. 1971;51:702–747. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

