Endogenous RGS14 is a cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling protein that localizes to juxtanuclear membranes and chromatin-rich regions of the nucleus
- PMID: 28934222
- PMCID: PMC5608220
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184497
Endogenous RGS14 is a cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling protein that localizes to juxtanuclear membranes and chromatin-rich regions of the nucleus
Abstract
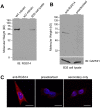
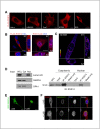
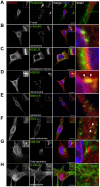
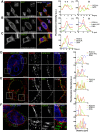
Regulator of G protein signaling 14 (RGS14) is a multifunctional scaffolding protein that integrates G protein and H-Ras/MAPkinase signaling pathways to regulate synaptic plasticity important for hippocampal learning and memory. However, to date, little is known about the subcellular distribution and roles of endogenous RGS14 in a neuronal cell line. Most of what is known about RGS14 cellular behavior is based on studies of tagged, recombinant RGS14 ectopically overexpressed in unnatural host cells. Here, we report for the first time a comprehensive assessment of the subcellular distribution and dynamic localization of endogenous RGS14 in rat B35 neuroblastoma cells. Using confocal imaging and 3D-structured illumination microscopy, we find that endogenous RGS14 localizes to subcellular compartments not previously recognized in studies of recombinant RGS14. RGS14 localization was observed most notably at juxtanuclear membranes encircling the nucleus, at nuclear pore complexes (NPC) on both sides of the nuclear envelope and within intranuclear membrane channels, and within both chromatin-poor and chromatin-rich regions of the nucleus in a cell cycle-dependent manner. In addition, a subset of nuclear RGS14 localized adjacent to active RNA polymerase II. Endogenous RGS14 was absent from the plasma membrane in resting cells; however, the protein could be trafficked to the plasma membrane from juxtanuclear membranes in endosomes derived from ER/Golgi, following constitutive activation of endogenous RGS14 G protein binding partners using AlF4¯. Finally, our findings show that endogenous RGS14 behaves as a cytoplasmic-nuclear shuttling protein confirming what has been shown previously for recombinant RGS14. Taken together, the findings highlight possible cellular roles for RGS14 not previously recognized that are distinct from the regulation of conventional GPCR-G protein signaling, in particular undefined roles for RGS14 in the nucleus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
14-3-3γ binds regulator of G protein signaling 14 (RGS14) at distinct sites to inhibit the RGS14:Gαi-AlF4- signaling complex and RGS14 nuclear localization.J Biol Chem. 2018 Sep 21;293(38):14616-14631. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002816. Epub 2018 Aug 9. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30093406 Free PMC article.
-
Human genetic variants disrupt RGS14 nuclear shuttling and regulation of LTP in hippocampal neurons.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100024. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.016009. Epub 2020 Nov 22. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33410399 Free PMC article.
-
RGS14 is a centrosomal and nuclear cytoplasmic shuttling protein that traffics to promyelocytic leukemia nuclear bodies following heat shock.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jan 7;280(1):805-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M408163200. Epub 2004 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15520006
-
RGS14 Regulation of Post-Synaptic Signaling and Spine Plasticity in Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 25;22(13):6823. doi: 10.3390/ijms22136823. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34201943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulator of G Protein Signaling 14: A Molecular Brake on Synaptic Plasticity Linked to Learning and Memory.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015;133:169-206. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2015. PMID: 26123307 Review.
Cited by
-
14-3-3γ binds regulator of G protein signaling 14 (RGS14) at distinct sites to inhibit the RGS14:Gαi-AlF4- signaling complex and RGS14 nuclear localization.J Biol Chem. 2018 Sep 21;293(38):14616-14631. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.002816. Epub 2018 Aug 9. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 30093406 Free PMC article.
-
Human genetic variants disrupt RGS14 nuclear shuttling and regulation of LTP in hippocampal neurons.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100024. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.016009. Epub 2020 Nov 22. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33410399 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Variants Associated with Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor 23.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018 Oct;29(10):2583-2592. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2018020192. Epub 2018 Sep 14. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30217807 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of mGluR-dependent plasticity in hippocampal area CA2.Hippocampus. 2023 Jun;33(6):730-744. doi: 10.1002/hipo.23529. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Hippocampus. 2023. PMID: 36971428 Free PMC article.
-
RGS14 limits seizure-induced mitochondrial oxidative stress and pathology in hippocampus.Neurobiol Dis. 2023 Jun 1;181:106128. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2023.106128. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Neurobiol Dis. 2023. PMID: 37075948 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hepler JR, Gilman AG (1992) G proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 17: 383–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90005-T - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hamm HE (1998) The many faces of G protein signaling. J Biol Chem 273: 669–672. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.2.669 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hollinger S, Hepler JR (2002) Cellular regulation of RGS proteins: modulators and integrators of G protein signaling. Pharmacol Rev 54: 527–559. doi: 10.1124/pr.54.3.527 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shu F, Ramineni S, Hepler JR (2010) RGS14 is a multifunctional scaffold that integrates G protein and Ras/Raf MAPkinase signalling pathways. Cell Signal 22: 366–376. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2009.10.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vellano CP, Brown NE, Blumer JB, Hepler JR (2013) Assembly and function of the regulator of G protein signaling 14 (RGS14)·H-Ras signaling complex in live cells are regulated by Gαi1 and Gαi-linked G protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem 288: 3620–3631. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.440057 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

