New experimental model for single liver lobe hyperthermia in small animals using non-directional microwaves
- PMID: 28934251
- PMCID: PMC5608293
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184810
New experimental model for single liver lobe hyperthermia in small animals using non-directional microwaves
Abstract
Purpose: Our aim was to develop a new experimental model for in vivo hyperthermia using non-directional microwaves, applicable to small experimental animals. We present an affordable approach for targeted microwave heat delivery to an isolated liver lobe in rat, which allows rapid, precise and stable tissue temperature control.
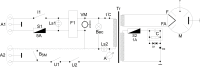
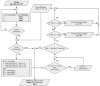
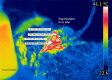
Materials and methods: A new experimental model is proposed. We used a commercial available magnetron generating 2450 MHz, with 4.4V and 14A in the filament and 4500V anodic voltage. Modifications were required in order to adjust tissue heating such as to prevent overheating and to allow for fine adjustments according to real-time target temperature. The heating is controlled using a virtual instrument application implemented in LabView® and responds to 0.1° C variations in the target. Ten healthy adult male Wistar rats, weighing 250-270 g were used in this study. The middle liver lobe was the target for controlled heating, while the rest of the living animal was protected.
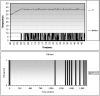
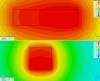
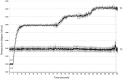
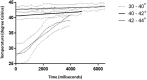
Results: In vivo microwave delivery using our experimental setting is safe for the animals. Target tissue temperature rises from 30°C to 40°C with 3.375°C / second (R2 = 0.9551), while the increment is lower it the next two intervals (40-42°C and 42-44°C) with 0.291°C/ s (R2 = 0.9337) and 0.136°C/ s (R2 = 0.7894) respectively, when testing in sequences. After reaching the desired temperature, controlled microwave delivery insures a very stable temperature during the experiments.
Conclusions: We have developed an inexpensive and easy to manufacture system for targeted hyperthermia using non-directional microwave radiation. This system allows for fine and stable temperature adjustments within the target tissue and is ideal for experimental models testing below or above threshold hyperthermia.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simulation-based design and characterization of a microwave applicator for MR-guided hyperthermia experimental studies in small animals.Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2020 Jan;6(1):015001. doi: 10.1088/2057-1976/ab36dd. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Biomed Phys Eng Express. 2020. PMID: 32999735 Free PMC article.
-
An easy-to-use microwave hyperthermia system combined with spatially resolved MR temperature maps: phantom and animal studies.J Surg Res. 2006 Sep;135(1):179-86. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2006.02.016. Epub 2006 Mar 31. J Surg Res. 2006. PMID: 16580694
-
Changes in muscle temperature induced by 434 MHz microwave hyperthermia.Br J Sports Med. 2007 Jul;41(7):425-9. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.2006.032540. Epub 2007 Jan 29. Br J Sports Med. 2007. PMID: 17261552 Free PMC article.
-
Metamaterial lens applicator for microwave hyperthermia of breast cancer.Int J Hyperthermia. 2009;25(6):434-45. doi: 10.1080/02656730903061609. Int J Hyperthermia. 2009. PMID: 19925323
-
Advances in Nanostructure-mediated Hyperthermia in Tumor Therapies.Curr Drug Metab. 2018;19(2):85-93. doi: 10.2174/1389200219666180129141757. Curr Drug Metab. 2018. PMID: 29380691 Review.
References
-
- Vernon CC, Hand JW, Field SB, Machin D, Whaley JB, van der Zee J, et al. Radiotherapy with or without hyperthermia in the treatment of superficial localized breast cancer: results from five randomized controlled trials. International Collaborative Hyperthermia Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1996; 35 (4): 731–44. - PubMed
-
- Maeta M, Koga S, Wada J, Yokoyama M, Kato N, Kawahara H, et al. Clinical evaluation of total-body hyperthermia combined with anticancer chemotherapy for far-advanced miscellaneous cancer in Japan. Cancer 1987; 59 (6): 1101–6. - PubMed
-
- Shari Lieberman, A review of Whole Body Hyperthermia and the experience of Klinik St. Georg, Townsend Letter, Aug/Sept 2009. Available from: https://www.thefreelibrary.com/A+review+of+whole+body+hyperthermia+and+t....
-
- Vertree RA1, Leeth A, Girouard M, Roach JD, Zwischenberger JB. Whole-body hyperthermia: a review of theory, design and application. Perfusion. 2002. July;17(4):279–90. doi: 10.1191/0267659102pf588oa - DOI - PubMed
-
- Herman TS, Sweets CC, White DM, Gerner EW. Effect of heating on lethality due to hyperthermia and selected chemotherapeutic drugs. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982. March; 68(3):487–91. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

