An analysis of beak shape variation in two ages of domestic turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo) using landmark-based geometric morphometrics
- PMID: 28934330
- PMCID: PMC5608350
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185159
An analysis of beak shape variation in two ages of domestic turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo) using landmark-based geometric morphometrics
Abstract
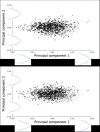
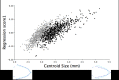
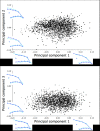
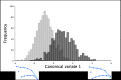
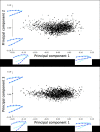
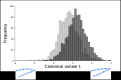
The objective of this study was to assess beak shape variation in domestic turkeys (Meleagris gallopavo) and determine the effects of age, sex, and beak size on beak shape variation using geometric morphometrics. Dorsal and right lateral images were taken of 2442 turkeys at 6 and 18.5 weeks of age. Landmarks were digitized in tpsDig in three analyses of the dorsal upper mandible, lateral upper mandible, and lateral lower mandible shape of each turkey at both ages. The coordinate data were then subjected to a principal components analysis (PCA), multivariate regression, and a canonical variates analysis (CVA) with a Procrustes ANOVA in MorphoJ. For the dorsal images, three principal components (PCs) showed beak shape variation ranged from long, narrow, and pointed to short, wide, and blunt upper mandibles at both ages (6 weeks: 95.36%, 18.5 weeks: 92.21%). Three PCs showed the lateral upper mandible shape variation ranged from long, wide beaks with long, curved beak tips to short, narrow beaks with short, pointed beak tips at both ages (6 weeks: 94.91%, 18.5 weeks: 94.33%). Three PCs also explained 97.80% (6 weeks) and 97.11% (18.5 weeks) of the lateral lower mandible shape variation ranging from wide and round to narrow and thin lower mandibles with superior/inferior beak tip shifts. Beak size accounted for varying proportions of the beak shape variation (0.96-54.76%; P < 0.0001) in the three analyses of each age group. For all the analyses, the CVA showed sexual dimorphism in beak shape (P < 0.0001) with female upper mandibles appearing wider and blunter dorsally with long, curved beak tips laterally. Whereas male turkey upper mandibles had a narrow, pointed dorsal appearance and short, pointed beak tips laterally. Future applications of beak shape variability could have a genetic and welfare value by incorporating beak shape variation to select for specific turkey beak phenotypes as an alternative to beak treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures










References
-
- Hocking P. Welfare of turkeys. In: Savory CJ, Hughes BO, editors. Proceedings of the Fourth European Symposium on Poultry Welfare. UK: Universities Federation for Animal Welfare; 1993. p. 125–38.
-
- Sherwin CM, Lewis PD, Perry GC. Effects of environmental enrichment fluorescent and intermittent lighting on injurious pecking amongst male turkey poults. Br Poult Sci. 1999;40: 592–8. doi: 10.1080/00071669986954 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Duggan G, Widowski TM, Quinton M, Torrey S. The development of injurious pecking in a commercial turkey facility. J Appl Poult Res. 2014;23: 280–90.
-
- Dalton HA, Wood BJ, Torrey S. Injurious pecking in domestic turkeys: development, causes, and potential solutions. World Poult Sci J. 2013;69: 865–76.
-
- Lewis PD, Perry GC, Sherwin CM. Effect of photoperiod and light intensity on the performance of intact male turkeys. Anim Sci. 1998;66: 759–67.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

