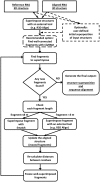
SupeRNAlign: a new tool for flexible superposition of homologous RNA structures and inference of accurate structure-based sequence alignments
- PMID: 28934487
- PMCID: PMC5766185
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx631
SupeRNAlign: a new tool for flexible superposition of homologous RNA structures and inference of accurate structure-based sequence alignments
Abstract
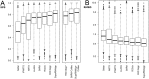
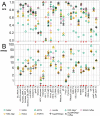
RNA has been found to play an ever-increasing role in a variety of biological processes. The function of most non-coding RNA molecules depends on their structure. Comparing and classifying macromolecular 3D structures is of crucial importance for structure-based function inference and it is used in the characterization of functional motifs and in structure prediction by comparative modeling. However, compared to the numerous methods for protein structure superposition, there are few tools dedicated to the superimposing of RNA 3D structures. Here, we present SupeRNAlign (v1.3.1), a new method for flexible superposition of RNA 3D structures, and SupeRNAlign-Coffee-a workflow that combines SupeRNAlign with T-Coffee for inferring structure-based sequence alignments. The methods have been benchmarked with eight other methods for RNA structural superposition and alignment. The benchmark included 151 structures from 32 RNA families (with a total of 1734 pairwise superpositions). The accuracy of superpositions was assessed by comparing structure-based sequence alignments to the reference alignments from the Rfam database. SupeRNAlign and SupeRNAlign-Coffee achieved significantly higher scores than most of the benchmarked methods: SupeRNAlign generated the most accurate sequence alignments among the structure superposition methods, and SupeRNAlign-Coffee performed best among the sequence alignment methods.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Murzin A.G., Brenner S.E., Hubbard T., Chothia C.. SCOP: a structural classification of proteins database for the investigation of sequences and structures. J. Mol. Biol. 1995; 247:536–540. - PubMed
-
- Orengo C.A., Michie A.D., Jones S., Jones D.T., Swindells M.B., Thornton J.M.. CATH–a hierarchic classification of protein domain structures. Structure. 1997; 5:1093–1108. - PubMed
-
- Holm L., Sander C.. Dali: a network tool for protein structure comparison. Trends Biochem. Sci. 1995; 20:478–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

