Antisense oligonucleotides targeting translation inhibitory elements in 5' UTRs can selectively increase protein levels
- PMID: 28934489
- PMCID: PMC5766168
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx632
Antisense oligonucleotides targeting translation inhibitory elements in 5' UTRs can selectively increase protein levels
Abstract
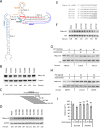
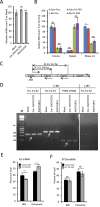
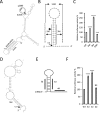
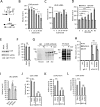
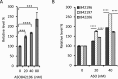
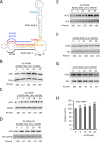
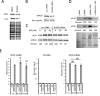
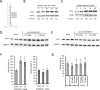
A variety of diseases are caused by deficiencies in amounts or activity of key proteins. An approach that increases the amount of a specific protein might be of therapeutic benefit. We reasoned that translation could be specifically enhanced using trans-acting agents that counter the function of negative regulatory elements present in the 5' UTRs of some mRNAs. We recently showed that translation can be enhanced by antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) that target upstream open reading frames. Here we report the amount of a protein can also be selectively increased using ASOs designed to hybridize to other translation inhibitory elements in 5' UTRs. Levels of human RNASEH1, LDLR, and ACP1 and of mouse ACP1 and ARF1 were increased up to 2.7-fold in different cell types and species upon treatment with chemically modified ASOs targeting 5' UTR inhibitory regions in the mRNAs encoding these proteins. The activities of ASOs in enhancing translation were sequence and position dependent and required helicase activity. The ASOs appear to improve the recruitment of translation initiation factors to the target mRNA. Importantly, ASOs targeting ACP1 mRNA significantly increased the level of ACP1 protein in mice, suggesting that this approach has therapeutic and research potentials.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Wilson J.A., Richardson C.D.. Future promise of siRNA and other nucleic acid based therapeutics for the treatment of chronic HCV. Infect. Disord. Drug Targets. 2006; 6:43–56. - PubMed
-
- Bennett C.F., Swayze E.E.. RNA targeting therapeutics: molecular mechanisms of antisense oligonucleotides as a therapeutic platform. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010; 50:259–293. - PubMed
-
- Crooke S.T.V.T.A., Lima W.F., Wu H.-J.. Crooke ST. Antisense Drug Technology - Principles, Strategies, and Applications. 2008; 2nd edn, Boca Raton: CRC Press; 3–46.
-
- Rossbach M. Small non-coding RNAs as novel therapeutics. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010; 10:361–368. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

