Behavioral approach and orbitofrontal cortical activity during decision-making in substance dependence
- PMID: 28934666
- PMCID: PMC5754220
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2017.08.024
Behavioral approach and orbitofrontal cortical activity during decision-making in substance dependence
Abstract
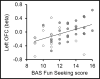
Behavioral approach, defined as behavior directed toward a reward or novel stimulus, when elevated, may increase one's vulnerability to substance use disorder. Behavioral approach has been associated with relatively greater left compared to right frontal activity; behavioral inhibition may be associated with relatively greater right compared to left frontal brain activity. We hypothesized that substance dependent individuals (SDI) would have higher behavioral approach than controls and greater prefrontal cortical activity during decision-making involving reward. We hypothesized that behavioral approach would correlate with left frontal activity during decision-making and that the correlation would be stronger in SDI than controls. 31 SDI and 21 controls completed the Behavioral Inhibition System/Behavioral Approach System (BIS/BAS) scales and performed a decision-making task during fMRI. Orbitofrontal (OFC) and dorsolateral prefrontal activity were correlated with BIS and BAS scores. Compared to controls, SDI had higher BAS Fun Seeking scores (p<0.001) and worse decision-making performance (p=0.004). BAS Fun Seeking correlated with left OFC activity during decision-making across group (r=0.444, p<0.003). The correlation did not differ by group. There was no correlation between BIS and right frontal activity. Left OFC may play a role in reward-related decision-making in substance use disorder especially in individuals with high behavioral approach.
Keywords: Behavioral approach; Behavioral inhibition; Bis/bas; Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC); Orbital frontal cortex (OFC); Substance dependence.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Influence of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and ventral striatum on risk avoidance in addiction: a mediation analysis.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015 Apr 1;149:10-7. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2014.12.026. Epub 2015 Feb 16. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2015. PMID: 25736619 Free PMC article.
-
Resting-state activity in the left executive control network is associated with behavioral approach and is increased in substance dependence.Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013 Apr 1;129(1-2):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2013.01.021. Epub 2013 Feb 19. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013. PMID: 23428318 Free PMC article.
-
Associating resting-state connectivity with trait impulsivity.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2017 Jun 1;12(6):1001-1008. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsx031. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28402539 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Heterogeneity within Rat Orbitofrontal Cortex in Reward Learning and Decision Making.J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 1;37(44):10529-10540. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1678-17.2017. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29093055 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural mechanisms of behavioral addiction: An ALE meta-analysis and MACM analysis.J Behav Addict. 2025 Jan 24;14(1):18-38. doi: 10.1556/2006.2024.00082. Print 2025 Mar 28. J Behav Addict. 2025. PMID: 39853319 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Motor Preparation Disrupts Proactive Control in the Stop Signal Task.Front Hum Neurosci. 2018 May 4;12:151. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00151. eCollection 2018. Front Hum Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29780308 Free PMC article.
-
Not all bad decisions are alike: approach and avoidant bad decisions are associated with distinct network organization.Front Neurosci. 2023 Oct 9;17:1249008. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1249008. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37877010 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between behavioral inhibition and approach motivation systems (BIS/BAS) and intrinsic brain network connectivity in adult cannabis users.Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2021 Sep 7;16(9):985-994. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsab054. Soc Cogn Affect Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34490458 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review on Common and Distinct Neural Correlates of Risk-taking in Substance-related and Non-substance Related Addictions.Neuropsychol Rev. 2023 Jun;33(2):492-513. doi: 10.1007/s11065-022-09552-5. Epub 2022 Jul 30. Neuropsychol Rev. 2023. PMID: 35906511 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Social Reward and Corticostriatal Connectivity in Substance Use.J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2020;5:e200024. doi: 10.20900/jpbs.20200024. Epub 2020 Oct 29. J Psychiatr Brain Sci. 2020. PMID: 33215046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abuse S. Mental Health Services Administration (2012) Results from the 2011 national survey on drug use and health: summary of national findings. NSDUH Ser H-44 HHS Publ No SMA 12-4713 2012
-
- Balconi M, Mazza G. Brain oscillations and BIS/BAS (behavioral inhibition/activation system) effects on processing masked emotional cues. ERS/ERD and coherence measures of alpha band. Int J Psychophysiol Off J Int Organ Psychophysiol. 2009;74:158–165. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2009.08.006. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

