EGFR Mutation Status in Lung Adenocarcinoma-Associated Malignant Pleural Effusion and Efficacy of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
- PMID: 28934846
- PMCID: PMC6056963
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2017.378
EGFR Mutation Status in Lung Adenocarcinoma-Associated Malignant Pleural Effusion and Efficacy of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
Abstract
Purpose: Malignant pleural effusions (MPEs) are often observed in lung cancer, particularly adenocarcinoma. The aim of this study was to investigate epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation status in lung adenocarcinoma-associated MPEs (LA-MPEs) and its correlation with efficacy of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy.
Materials and methods: Samples comprised 40 cell blocks of pathologically-confirmed LA-MPEs collected before the start of EGFR TKI therapy. EGFR mutation status was re-evaluated by peptide nucleic acid clamping and the clinical outcomes of EGFR TKI‒treated patients were analyzed retrospectively.
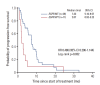
Results: EGFR mutations were detected in 72.5% of LA-MPE cell blocks (29/40). The median progression-free survival for patients with EGFR mutations in LA-MPEs was better than that for patients with wild-type EGFR (7.33 months vs. 2.07 months; hazard ratio, 0.486; 95% confidence interval, 0.206 to 1.144; p=0.032). The objective response rate (ORR) of 26 patients with EGFR mutations in LA-MPEs among the 36 patients with measurable lesions was 80.8%, while the ORR of the 10 patients with wild-type EGFR in LA-MPEs was 10% (p < 0.001). Among the 26 patients with EGFR mutations in LA-MPEs, the ORR of target lesions and LA-MPEs were 88.5% and 61.5%, respectively (p=0.026).
Conclusion: EGFR mutation status in cell blocks of LA-MPEs confirmed by pathologic diagnosis is highly predictive of EGFR TKI efficacy. For patients with EGFR mutations in LA-MPEs, the response to EGFR TKIs seems to be worse for pleural effusions than for solid tumors.
Keywords: Lung adenocarcinoma; Pleural effusion; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor; Epidermal growth factor receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest relevant to this article was not reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Malignant pleural effusion supernatants are substitutes for metastatic pleural tumor tissues in EGFR mutation test in patients with advanced lung adenocarcinoma.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 28;9(2):e89946. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089946. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24587142 Free PMC article.
-
Survival of lung adenocarcinoma patients with malignant pleural effusion.Eur Respir J. 2013 Jun;41(6):1409-18. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00069812. Epub 2012 Sep 27. Eur Respir J. 2013. PMID: 23018906
-
Can EGFR-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKI) Alone Without Talc Pleurodesis Prevent Recurrence of Malignant Pleural Effusion (MPE) in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2016;13(2):68-76. doi: 10.2174/1570163813666160524142846. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2016. PMID: 27216707 Free PMC article.
-
The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of malignant pleural effusion.Curr Oncol Rep. 2013 Jun;15(3):207-16. doi: 10.1007/s11912-013-0315-7. Curr Oncol Rep. 2013. PMID: 23568600 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of elemene in treating malignant pleural effusion caused by tumors: A PRISMA guided meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(44):e12542. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012542. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30383624 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sensitive molecular testing methods can demonstrate NSCLC driver mutations in malignant pleural effusion despite non-malignant cytology.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2019 Aug;8(4):513-518. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2019.07.05. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31555523 Free PMC article.
-
Failure pattern and radiotherapy exploration in malignant pleural effusion non-small cell lung cancer treated with targeted therapy.Front Oncol. 2023 May 19;13:974735. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.974735. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37274290 Free PMC article.
-
EGFR Mutation is a Prognostic Factor in Lung Cancer Patients with Pleural Dissemination Detected During or After Surgery.Ann Surg Oncol. 2023 Oct;30(11):6697-6702. doi: 10.1245/s10434-023-13791-y. Epub 2023 Jun 25. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37355521 Free PMC article.
-
Pleural effusions associated with squamous cell lung carcinoma have a low diagnostic yield and a poor prognosis.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021 Jun;10(6):2500-2508. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-21-123. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34295657 Free PMC article.
-
Malignant pleural effusion diagnosis and therapy.Open Life Sci. 2023 Feb 28;18(1):20220575. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0575. eCollection 2023. Open Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36874629 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Spiro SG, Silvestri GA. One hundred years of lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005;172:523–9. - PubMed
-
- Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, Langer C, Sandler A, Krook J, et al. Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:92–6. - PubMed
-
- Tan DS, Yom SS, Tsao MS, Pass HI, Kelly K, Peled N, et al. The International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer consensus statement on optimizing management of EGFR mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer: status in 2016. J Thorac Oncol. 2016;11:946–63. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

