Spontaneous Development of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Mice with Cell-specific Deletion of Inhibitor of κB Kinase 2
- PMID: 28935002
- PMCID: PMC5621568
Spontaneous Development of Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Mice with Cell-specific Deletion of Inhibitor of κB Kinase 2
Abstract
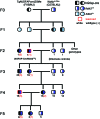
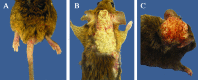
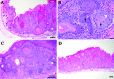
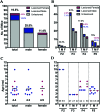
The deletion of NFκB in epithelial tissues by using skin-specific promoters can cause both tumor formation and severe inflammatory dermatitis, indicating that this signaling pathway is important for the maintenance of immune homeostasis in epithelial tissues. In the present study, we crossed mice transgenic for loxP-Ikbk2 and human Gfap-cre to selectively delete IKK2 in CNS astrocytes. Unexpectedly, a subset of mice developed severe and progressive skin lesions marked by hyperplasia, hyperkeratosis, dysplasia, inflammation, and neoplasia with a subset of lesions diagnosed as squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). The development of lesions was monitored over a 3.5-y period and over 4 filial generations. Average age of onset of was 4 mo of age with 19.5% of mice affected with frequency increasing in progressive generations. Lesion development appeared to correlate not only with unintended IKK2 deletion in GFAP expressing cells of the epidermis, but also with increased expression of TNF in lesioned skin. The skins changes described in these animals are similar to those in transgenic mice with an epidermis-specific deletion of NFκB and thus represents another genetic mouse model that can be used to study the role of NFκB signaling in regulating the development of SCC.
Figures
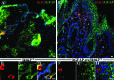
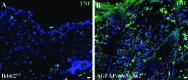
References
-
- Banno T, Gazel A, Blumemberg M. 2005. Pathway-specific profiling identifies the NFκB-dependent tumor necrosis factor α-regulated genes in epidermal keratinocytes. J Biol Chem 280: 18973–18980. - PubMed
-
- Bonizzi G, Karin M. 2004. The 2 NFκB activation pathways and their role in innate and adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol 25:280–288. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
