Suppression of ERK signalling abolishes primitive endoderm formation but does not promote pluripotency in rabbit embryo
- PMID: 28935706
- PMCID: PMC5675450
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.156406
Suppression of ERK signalling abolishes primitive endoderm formation but does not promote pluripotency in rabbit embryo
Abstract
Formation of epiblast (EPI) - the founder line of all embryonic lineages - and extra-embryonic supportive tissues is one of the key events in mammalian development. The prevailing model of early mammalian development is based almost exclusively on the mouse. Here, we provide a comprehensive, stage-by-stage analysis of EPI and extra-embryonic primitive endoderm (PrE) formation during preimplantation development of the rabbit. Although we observed that rabbit embryos have several features in common with mouse embryos, including a stage-related initiation of lineage specification, our results demonstrate the existence of some key differences in lineage specification among mammals. Contrary to the current view, our data suggest that reciprocal repression of GATA6 and NANOG is not fundamental for the initial stages of PrE versus EPI specification in mammals. Furthermore, our results provide insight into the observed discrepancies relating to the role of FGF/ERK signalling in PrE versus EPI specification between mouse and other mammals.
Keywords: Blastocyst; Epiblast; FGF; Primitive endoderm; Rabbit.
© 2017. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
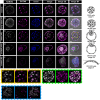
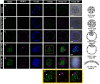
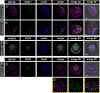

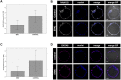
Similar articles
-
Gata6, Nanog and Erk signaling control cell fate in the inner cell mass through a tristable regulatory network.Development. 2014 Oct;141(19):3637-48. doi: 10.1242/dev.109678. Epub 2014 Sep 10. Development. 2014. PMID: 25209243
-
PI3K/AKT signaling controls ICM maturation and proper epiblast and primitive endoderm specification in mice.Dev Cell. 2025 Jan 20;60(2):204-219.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.10.001. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Dev Cell. 2025. PMID: 39461340
-
GATA6 levels modulate primitive endoderm cell fate choice and timing in the mouse blastocyst.Dev Cell. 2014 May 27;29(4):454-67. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2014.04.011. Epub 2014 May 15. Dev Cell. 2014. PMID: 24835466 Free PMC article.
-
[Epiblast and primitive endoderm cell specification during mouse preimplantation development: a combination between biology and mathematical modeling].Med Sci (Paris). 2016 Feb;32(2):192-7. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20163202013. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Med Sci (Paris). 2016. PMID: 26936177 Review. French.
-
Primitive Endoderm Differentiation: From Specification to Epithelialization.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2018;128:81-104. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2017.12.001. Epub 2018 Feb 2. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2018. PMID: 29477172 Review.
Cited by
-
Pluripotency and Growth Factors in Early Embryonic Development of Mammals: A Comparative Approach.Vet Sci. 2021 May 4;8(5):78. doi: 10.3390/vetsci8050078. Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34064445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Growth-factor-mediated coupling between lineage size and cell fate choice underlies robustness of mammalian development.Elife. 2020 Jul 28;9:e56079. doi: 10.7554/eLife.56079. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32720894 Free PMC article.
-
ERK inhibition promotes neuroectodermal precursor commitment by blocking self-renewal and primitive streak formation of the epiblast.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018 Jan 5;9(1):2. doi: 10.1186/s13287-017-0750-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 29304842 Free PMC article.
-
MED20 is essential for early embryogenesis and regulates NANOG expression.Reproduction. 2019 Mar;157(3):215-222. doi: 10.1530/REP-18-0508. Reproduction. 2019. PMID: 30571656 Free PMC article.
-
From genes to environment in shaping of an embryo: understanding embryonic-extraembryonic interactions at the BSDB autumn meeting in Oxford.Dev Genes Evol. 2019 May;229(2-3):83-87. doi: 10.1007/s00427-019-00628-6. Epub 2019 Feb 23. Dev Genes Evol. 2019. PMID: 30798362 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Acampora D., Omodei D., Petrosino G., Garofalo A., Savarese M., Nigro V., Di Giovannantonio L. G., Mercadante V. and Simeone A. (2016). Loss of the Otx2-binding site in the Nanog promoter affects the integrity of embryonic stem cell subtypes and specification of inner cell mass-derived epiblast. Cell Rep. 15, 2651-2664. 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.05.041 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

