Absolute quantitation of disease protein biomarkers in a single LC-MS acquisition using apolipoprotein F as an example
- PMID: 28935895
- PMCID: PMC5608892
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12229-2
Absolute quantitation of disease protein biomarkers in a single LC-MS acquisition using apolipoprotein F as an example
Abstract
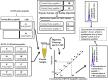
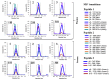
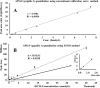
LC-MS and immunoassay can detect protein biomarkers. Immunoassays are more commonly used but can potentially be outperformed by LC-MS. These techniques have limitations including the necessity to generate separate calibration curves for each biomarker. We present a rapid mass spectrometry-based assay utilising a universal calibration curve. For the first time we analyse clinical samples using the HeavyPeptide IGNIS kit which establishes a 6-point calibration curve and determines the biomarker concentration in a single LC-MS acquisition. IGNIS was tested using apolipoprotein F (APO-F), a potential biomarker for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Human serum and IGNIS prime peptides were digested and the IGNIS assay was used to quantify APO-F in clinical samples. Digestion of IGNIS prime peptides was optimised using trypsin and SMART Digest™. IGNIS was 9 times faster than the conventional LC-MS method for determining the concentration of APO-F in serum. APO-F decreased across NAFLD stages. Inter/intra-day variation and stability post sample preparation for one of the peptides was ≤13% coefficient of variation (CV). SMART Digest™ enabled complete digestion in 30 minutes compared to 24 hours using in-solution trypsin digestion. We have optimised the IGNIS kit to quantify APO-F as a NAFLD biomarker in serum using a single LC-MS acquisition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Rifai N, Ridker PM. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein: a novel and promising marker of coronary heart disease. Clin Chem. 2001;47:403–411. - PubMed
-
- Ramamohan V, Abbott JT, Klee GG, Yih Y. Modeling the effect of instrument drift in clinical laboratories: A serum bilirubin assay case study. IIE Transactions on Healthcare Systems Engineering. 2015;5:147–164. doi: 10.1080/19488300.2015.1060551. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

