Differential regulation of Effector and Regulatory T cell function by Blimp1
- PMID: 28935958
- PMCID: PMC5608714
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12171-3
Differential regulation of Effector and Regulatory T cell function by Blimp1
Abstract
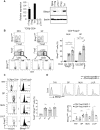
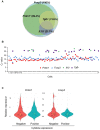
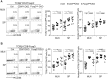
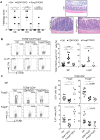
The transcriptional regulator Blimp1 plays crucial roles in controlling terminal differentiation in several lineages. In T cells, Blimp1 is expressed in both effector (Teff) and regulatory (Treg) cells, and mice with T cell-specific deletion of Blimp1 (Blimp1CKO mice) spontaneously develop severe intestinal inflammation, indicating a crucial role for Blimp1 in T cell homeostasis regulation. Blimp1 has been shown to function as a direct activator of the Il10 gene and although its requirement for IL10 expression has been demonstrated in both Treg and Teff cells under inflammatory conditions, the intrinsic requirement of Blimp1 for homeostatic maintenance of these T cell subsets had not been investigated. Using mice with Foxp3+ Treg-cell specific deletion of Blimp1 and other approaches, here we show that Foxp3+ Treg cell-intrinsic expression of Blimp1 is required to control Treg and Teff cells homeostasis but, unexpectedly, it is dispensable to prevent development of severe spontaneous intestinal inflammation. In addition, we show that Blimp1 controls common and unique aspects of Treg and Teff cell function by differentially regulating gene expression in these T cell subsets. These findings document previously unappreciated aspects of Blimp1's role in T cell biology and shed light on the intricate mechanisms regulating Treg and Teff cell function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Cretney, E. et al. The transcription factors Blimp-1 and IRF4 jointly control the differentiation and function of effector regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol 12, 304-311. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

