Refabrication of an implant-retained auricular prosthesis using clip attachment pickup technique
- PMID: 28936047
- PMCID: PMC5601500
- DOI: 10.4103/jips.jips_227_16
Refabrication of an implant-retained auricular prosthesis using clip attachment pickup technique
Abstract
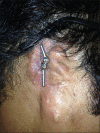
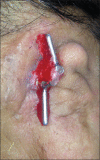
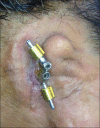
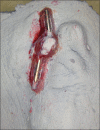
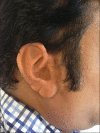
Increased patient acceptance and widespread use have led to a greater demand for refabrication of existing maxillofacial prostheses exhibiting wear and tear. Refabricating an osseointegrated implant-retained silicone auricular prosthesis on the existing Hader bar is a challenging task if it is performed without removing it. Therefore, an attachment level impression method is utilized for the refabrication of a new prosthesis on an existing Hader bar framework without removing it from the patient's defect. This case report discusses a modification of the Mahidol University technique. This modification provides a simple, speedy, and convenient method through which the relation between the metal framework and attachments could be obtained precisely. This precision allowed for easy fabrication of the acrylic housing, which in turn results in better adaptation of the auricular prosthesis to the patient's face. Therefore, this technique offers advantages to both the prosthetist in fabrication and the patient in facilitating him continue to wear his existing implant-retained prosthesis during refabrication process.
Keywords: Attachment level impression; craniofacial implants; implant retention; indirect acrylic housing; silicone auricular prosthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Implant retained auricular prosthesis with a modified hader bar: a case report.J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2014 Jun;14(2):187-90. doi: 10.1007/s13191-013-0277-3. Epub 2013 Mar 21. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2014. PMID: 24757357 Free PMC article.
-
Fabrication of a new silicone auricular prosthesis without removing the existing metallic framework.J Prosthet Dent. 2014 Dec;112(6):1605-8. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2014.05.020. Epub 2014 Jul 4. J Prosthet Dent. 2014. PMID: 24998323
-
Retention and load transfer characteristics of implant-retained auricular prostheses.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2007 May-Jun;22(3):366-72. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2007. PMID: 17622002
-
Retention systems for extraoral maxillofacial prosthetic implants: a critical review.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017 Oct;55(8):763-769. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2017.04.012. Epub 2017 May 25. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017. PMID: 28552609 Review.
-
Prosthesis auricular with osseointegrated implants and quality of life.J Craniofac Surg. 2010 Jan;21(1):94-6. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e3181c4651a. J Craniofac Surg. 2010. PMID: 20061968 Review.
Cited by
-
Utilizing DICOM data to generate custom computer-aided designing and computer-aided machining polyetheretherketone healing abutments for an ear prosthesis.J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2020 Oct-Dec;20(4):431-435. doi: 10.4103/jips.jips_62_20. Epub 2020 Oct 8. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2020. PMID: 33487972 Free PMC article.
-
Chondrogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells Induced by Decellularized Cartilage Matrix/Silk Fibroin Secondary Crosslinking Hydrogel Scaffolds with a Three-Dimensional Microstructure.Polymers (Basel). 2023 Apr 13;15(8):1868. doi: 10.3390/polym15081868. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37112015 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rocke DJ, Tucci DL, Marcus J, McClennen J, Kaylie D. Osseointegrated implants for auricular defects: Operative techniques and complication management. Otol Neurotol. 2014;35:1609–14. - PubMed
-
- Beumer J 3rd, Ma T, Marunick M, Roumanas E. Restoration of facial defects: Etiology, disability, and rehabilitation. In: Beumer J 3rd, editor. Maxillofacial Rehabilitation: Prosthodontic and Surgical Considerations. St. Louis: Ishiyaku EuroAmerica, Inc; 1996.
-
- Chotprasert N, Srithavaj T, Santawisuk W, Hovichitr W, Visuttiwattanakorn S. Implant-retained auricular prosthesis in a young patient, 6 years follow-up: A clinical report. Mahidol Dent J. 2007;27:217–22.
-
- Srithavaj T, Wijitworawong A, Kharel A, Sanohkann S, Santawisuk W. Attachment use in designing a stable facial prosthesis: A new clinical and technical report. Mahidol Dent J. 2006;26:337–43.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
