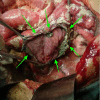
Not a Common Rectosigmoid Perforation
- PMID: 28936377
- PMCID: PMC5597061
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1465
Not a Common Rectosigmoid Perforation
Abstract
Gastrointestinal perforation is a common complication arising due to homicidal injuries, trauma or intake of medications like aspirin. Intestinal perforation caused by chronic intake of mud, clay or soil is a rare phenomenon and very few cases have been reported in the literature. We hereby present the first case of rectosigmoid perforation from Pakistan which was caused by chronic mud intake in a female patient. Diagnosis of this condition in its early stage is important because it can be fatal if not addressed urgently.
Keywords: geophagia; mud; perforation; rectosigmoid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Hawass NE, Alnozha MM, Kolawole TA. Trop Geogr Med. Vol. 39. Apr: 1987. Adult geophagia--report of three cases with review of the literature; pp. 191–195. - PubMed
-
- Spontaneous perforation of the rectum with possible stercoral etiology: report of a case and review of the literature. Tokunaga Y, Hata K, Nishitai R, et al. Surg Today. 1998;28:937–939. - PubMed
-
- Spontaneous perforation of rectum and rectosigmoid junction. Case report. Demirağ A, Nurlu H, Gürer A, et al. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/8412343. Mater Med Pol. 1993;25:47–48. - PubMed
-
- Perforation of the sigmoid colon due to geophagia. Woywodt A, Kiss A. Arch Surg. 1999;134:88–89. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources