TRPC3 Channels in Cardiac Fibrosis
- PMID: 28936433
- PMCID: PMC5594069
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2017.00056
TRPC3 Channels in Cardiac Fibrosis
Abstract
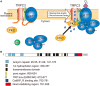
Cardiac stiffness, caused by interstitial fibrosis due to deposition of extracellular matrix proteins, is thought as a major clinical outcome of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). Canonical transient receptor potential (TRPC) subfamily proteins are components of Ca2+-permeable non-selective cation channels activated by receptor stimulation and mechanical stress, and have been attracted attention as a key mediator of maladaptive cardiac remodeling. How TRPC-mediated local Ca2+ influx encodes a specific signal to induce maladaptive cardiac remodeling has been long obscure, but our recent studies suggest a pathophysiological significance of channel activity-independent function of TRPC proteins for amplifying redox signaling in heart. This review introduces the current understanding of the physiological and pathophysiological roles of TRPCs, especially focuses on the role of TRPC3 as a positive regulator of reactive oxygen species (PRROS) in heart. We have revealed that TRPC3 stabilizes NADPH oxidase 2 (Nox2), a membrane-bound reactive oxygen species (ROS)-generating enzyme, by forming stable protein complex with Nox2, which leads to amplification of mechanical stress-induced ROS signaling in cardiomyocytes, resulting in induction of fibrotic responses in cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts. Thus, the TRPC3 function as PRROS will offer a new therapeutic strategy for the prevention or treatment of HFpEF.
Keywords: Ca2+; NADPH oxidase; canonical transient receptor potential; cardiac fibrosis; cardiac remodeling; reactive oxygen species.
Figures


References
-
- Nishida M, Onohara N, Sato Y, Suda R, Ogushi M, Tanabe S, et al. Gα12/13-mediated up-regulation of TRPC6 negatively regulates endothelin-1-induced cardiac myofibroblast formation and collagen synthesis through nuclear factor of activated T cells activation. J Biol Chem (2007) 282(32):23117–28. 10.1074/jbc.M611780200 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

