Ex vivo lung perfusion review of a revolutionary technology
- PMID: 28936437
- PMCID: PMC5599284
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2017.07.17
Ex vivo lung perfusion review of a revolutionary technology
Abstract
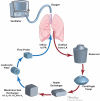
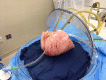
Donor lung shortage has been the main reason to the increasing number of patients waiting for lung transplant. Ex vivo lung perfusion (EVLP) is widely expanding technology to assess and prepare the lungs who are considered marginal for transplantation. the outcomes are encouraging and comparable to the lungs transplanted according to the standard criteria. in this article, we will discuss the history of development, the techniques and protocols of ex vivo, and the logics and rationales for ex vivo use.
Keywords: Ex vivo lung perfusion (EVLP); ex vivo; lung reconditioning; lung transplant.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources