SMC complexes orchestrate the mitotic chromatin interaction landscape
- PMID: 28936767
- PMCID: PMC5851691
- DOI: 10.1007/s00294-017-0755-y
SMC complexes orchestrate the mitotic chromatin interaction landscape
Abstract
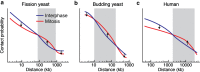
Chromatin is a very long DNA-protein complex that controls the expression and inheritance of the genetic information. Chromatin is stored within the nucleus in interphase and further compacted into chromosomes during mitosis. This process, known as chromosome condensation, is essential for faithful segregation of genomic DNA into daughter cells. Condensin and cohesin, members of the structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) family, are fundamental for chromosome architecture, both for establishment of chromatin structure in the interphase nucleus and for the formation of condensed chromosomes in mitosis. These ring-shaped SMC complexes are thought to regulate the interactions between DNA strands by topologically entrapping DNA. How this activity shapes chromosomes is not yet understood. Recent high throughput chromosome conformation capture studies revealed how chromatin is reorganized during the cell cycle and have started to explore the role of SMC complexes in mitotic chromatin architecture. Here, we summarize these findings and discuss the conserved nature of chromosome condensation in eukaryotes. We highlight the unexpected finding that condensin-dependent intra-chromosomal interactions in mitosis increase within a distinctive distance range that is characteristic for an organism, while longer and shorter-range interactions are suppressed. This reveals important molecular insight into chromosome architecture.
Keywords: Cell cycle; Chromatin; Chromosome condensation; Hi-C; SMC complex.
Figures
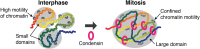
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

