NMDA Receptors and NO:cGMP Signaling Pathway Mediate the Diazepam-Induced Sensitization to Withdrawal Signs in Mice
- PMID: 28936791
- PMCID: PMC5766724
- DOI: 10.1007/s12640-017-9810-1
NMDA Receptors and NO:cGMP Signaling Pathway Mediate the Diazepam-Induced Sensitization to Withdrawal Signs in Mice
Abstract
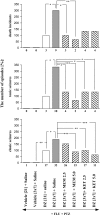
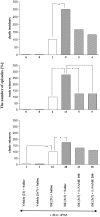
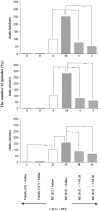
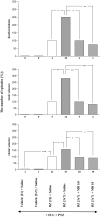
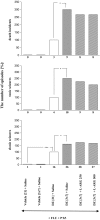
The goal of the present study was to examine the effects of N-methyl-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonists-memantine and ketamine and the drugs modifying the NO:cGMP pathway-NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) and 7-nitroindazole (7-NI), the endogenous precursor of NO-L-arginine, and the guanylyl cyclase inhibitor-methylene blue (MB) on the development of sensitization to withdrawal signs precipitated after chronic, interrupted treatment with diazepam, a benzodiazepine receptor agonist, in mice. To develop the sensitization, the mice were divided into groups: continuously and sporadically (with two diazepam-free periods) treated with diazepam (15 mg/kg, sc). To precipitate the withdrawal syndrome (clonic and tonic seizures, and death), pentylenetetrazole (55 mg/kg, sc) with the benzodiazepine receptor antagonist, flumazenil (5.0 mg/kg, ip), were administered after the last injection of diazepam or saline. Memantine (2.5, 5.0 mg/kg), and ketamine (2.5, 5.0 mg/kg), L-NAME (100, 200 mg/kg) and 7-NI (20 and 40 mg/kg), L-arginine (250, 500 mg/kg) and MB (5 and 10 mg/kg) were administered ip in sporadically diazepam-treated mice during the diazepam-free periods. Our results indicated that both NMDA receptor antagonists and drugs that inhibit the NO:cGMP pathway, except L-arginine (the endogenous donor of NO), attenuated the diazepam-induced sensitization to withdrawal signs in mice. Thus, NMDA receptors and the NO:cGMP pathway are involved in the mechanisms of sensitization to benzodiazepine withdrawal.
Keywords: Diazepam; NMDA receptor; NO:cGMP pathway; Sensitization; Withdrawal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The proconvulsant effect of sildenafil in mice: role of nitric oxide-cGMP pathway.Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Apr;147(8):935-43. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706680. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16474413 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressant effect of pramipexole in mice forced swimming test: A cross talk between dopamine receptor and NMDA/nitric oxide/cGMP pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Jul;81:295-304. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.04.026. Epub 2016 Apr 23. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27261607
-
Participation of the GABA/benzodiazepine receptor and the NO-cyclicGMP pathway in the "antinociceptive-like effects" of diazepam.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008 Nov;91(1):128-33. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2008.06.021. Epub 2008 Jun 30. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008. PMID: 18638499
-
Role of nitric oxide in anticonvulsant effects of benzodiazepines in mice.Pol J Pharmacol. 2003 Mar-Apr;55(2):181-91. Pol J Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12926545
-
Contribution of glutamate receptors to benzodiazepine withdrawal signs.Jpn J Pharmacol. 1999 Sep;81(1):1-6. doi: 10.1254/jjp.81.1. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1999. PMID: 10580363 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological evidence for glutamatergic pathway involvement in the antidepressant-like effects of 2-phenyl-3-(phenylselanyl)benzofuran in male Swiss mice.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Nov;396(11):3033-3044. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02508-3. Epub 2023 May 9. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37160481
-
Intravenous ketamine for benzodiazepine deprescription and withdrawal management in treatment-resistant depression: a preliminary report.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023 Nov;48(12):1769-1777. doi: 10.1038/s41386-023-01689-y. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37532888 Free PMC article.
-
NMDA receptors and L-arginine/nitric oxide/cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway contribute to the antidepressant-like effect of Yueju pill in mice.Biosci Rep. 2019 Sep 16;39(9):BSR20190524. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190524. Print 2019 Sep 30. Biosci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31467174 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

