Visualization of lumbar nerves using reduced field of view diffusion tensor imaging in healthy volunteers and patients with degenerative lumbar disorders
- PMID: 28937274
- PMCID: PMC6047648
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20160929
Visualization of lumbar nerves using reduced field of view diffusion tensor imaging in healthy volunteers and patients with degenerative lumbar disorders
Abstract
Objective: We investigated high resolution diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of lumbar nerves with reduced field of view (rFOV) using 3 T MRI.
Methods: DTI measured with rFOV was compared with conventional FOV (cFOV) 3.0 T MRI in 5 healthy volunteers and 10 patients with degenerative lumbar disorders. The intracanal, foramina and extraforamina of the L5 nerve were established as the regions of interest and fractional anisotropy (FA) values and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values were measured. Image quality for tractography and FA maps and ADC maps, interindividual and intraindividual reliability of FA and ADC, and signal-to-noise (SNR) were studied.
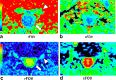
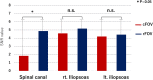
Results: Both of image qualities with tractography, FA map and ADC map showed that lumbar nerves were more clearly imaged with the rFOV. Intraindividual reliability was higher with rFOV compared with the conventional method for ADC values, while interindividual reliability was higher for both FA values and ADC values with the rFOV method over the conventional method (p < 0.05). Significantly higher SNR was obtained with rFOV compared with cFOV in the spinal canal (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: rFOV enabled clearer imaging of the lumbar nerve, allowing for more accurate measurement of FA and ADC values. Significantly higher SNR was obtained with rFOV compared with cFOV in the spinal canal. To our knowledge, this research showed for the first time the usefulness of rFOV in patients with degenerative lumbar disorders. High resolution DTI using rFOV may become useful in clinical applications because visualization of nerve entrapments and quantification of DTI parameters may allow more accurate diagnoses of lumbar nerve dysfunction. Advances in knowledge: Compared with traditional methods, rFOV allows for clear imaging of the lumbar nerve and enables accurate measurements of the FA and ADC values. High-resolution DTI with rFOV may be used to visualize nerve entrapments and allow for more accurate diagnosis of DTI parameter quantification with opportunities for clinical applications.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The diagnosis of double-crush lesion in the L5 lumbar nerve using diffusion tensor imaging.Spine J. 2016 Mar;16(3):315-21. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Spine J. 2016. PMID: 26592484
-
Assessment of reduced field of view in diffusion tensor imaging of the lumbar nerve roots at 3 T.Eur Radiol. 2013 May;23(5):1361-6. doi: 10.1007/s00330-012-2710-0. Epub 2012 Nov 18. Eur Radiol. 2013. PMID: 23179524
-
Diffusion tensor imaging of lumbar spinal nerve in subjects with degenerative lumbar disorders.Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 Oct;33(8):956-61. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2015.05.002. Epub 2015 May 12. Magn Reson Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25979227
-
Recent advances in magnetic resonance neuroimaging of lumbar nerve to clinical applications: A review of clinical studies utilizing Diffusion Tensor Imaging and Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance neurography.Spine Surg Relat Res. 2017 Dec 20;1(2):61-71. doi: 10.22603/ssrr.1.2016-0015. eCollection 2017. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2017. PMID: 31440614 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diffusion tensor imaging of peripheral nerves.Skeletal Radiol. 2010 Nov;39(11):1073-9. doi: 10.1007/s00256-010-0974-5. Epub 2010 Jul 1. Skeletal Radiol. 2010. PMID: 20593175 Review.
Cited by
-
Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Spinal Canal in Quantitative Assessment of Patients with Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis.Asian Spine J. 2021 Apr;15(2):207-215. doi: 10.31616/asj.2020.0026. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Asian Spine J. 2021. PMID: 32872759 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of radiological parameters associated with decreased fractional anisotropy values on diffusion tensor imaging in patients with lumbar spinal stenosis.Eur Spine J. 2019 Jun;28(6):1397-1405. doi: 10.1007/s00586-018-5562-8. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Eur Spine J. 2019. PMID: 29700619
-
Evaluating Spinal Canal Lesions Using Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Maps with Diffusion-Weighted Imaging.Asian Spine J. 2020 Jun;14(3):312-319. doi: 10.31616/asj.2019.0266. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Asian Spine J. 2020. PMID: 32050309 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of image quality of diffusion weighted readout segmentation of long variable echo-trains MR pulse sequence for lumbosacral nerve imaging at 3T.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Jan 1;13(1):196-209. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-191. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 36620175 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Assessment of Lumbar Nerve Roots Using Coronal-plane Single-shot Turbo Spin-echo Diffusion Tensor Imaging.Magn Reson Med Sci. 2020 May 1;19(2):159-165. doi: 10.2463/mrms.tn.2019-0014. Epub 2019 Jun 13. Magn Reson Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 31189790 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

