µ-Conotoxins Modulating Sodium Currents in Pain Perception and Transmission: A Therapeutic Potential
- PMID: 28937587
- PMCID: PMC5666403
- DOI: 10.3390/md15100295
µ-Conotoxins Modulating Sodium Currents in Pain Perception and Transmission: A Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
The Conus genus includes around 500 species of marine mollusks with a peculiar production of venomous peptides known as conotoxins (CTX). Each species is able to produce up to 200 different biological active peptides. Common structure of CTX is the low number of amino acids stabilized by disulfide bridges and post-translational modifications that give rise to different isoforms. µ and µO-CTX are two isoforms that specifically target voltage-gated sodium channels. These, by inducing the entrance of sodium ions in the cell, modulate the neuronal excitability by depolarizing plasma membrane and propagating the action potential. Hyperexcitability and mutations of sodium channels are responsible for perception and transmission of inflammatory and neuropathic pain states. In this review, we describe the current knowledge of µ-CTX interacting with the different sodium channels subtypes, the mechanism of action and their potential therapeutic use as analgesic compounds in the clinical management of pain conditions.
Keywords: conotoxin; ion current; pain transmission; sodium channel; µ-conotoxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
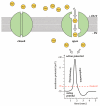

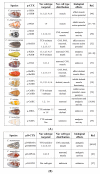
References
-
- Layer R.T., McIntosh J.M. Conotoxins: Therapeutic potential and application. Mar. Drugs. 2006;4:119–142. doi: 10.3390/md403119. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

