The Effect of RANKL/OPG Balance on Reducing Implant Complications
- PMID: 28937598
- PMCID: PMC5748549
- DOI: 10.3390/jfb8040042
The Effect of RANKL/OPG Balance on Reducing Implant Complications
Abstract
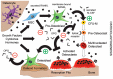
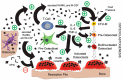
Despite the phenomenal success of implants particularly in the realms of dentistry and orthopaedics, there are still challenges to overcome. The failure of implants resulting from infection, prosthetic loosening, and non-union continue to be the most notorious examples. The cascade of fracture healing and bone repair, especially with the presence of an implant, is complex because it involves a multifaceted immune response alongside the intricate process of bone formation and remodelling. Bone loss is a serious clinical problem that is frequently accompanied by chronic inflammation, illustrating that there is a convoluted relationship between inflammation and bone erosion. The effects of pro-inflammatory factors play a significant role in initiating and maintaining osteoclastogenesis that results in bone resorption by osteoclasts. This is because there is a disruption of the relative ratio between Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor κB-Ligand (RANKL) and osteoprotegerin (OPG), which is central to modulating bone repair and remodelling. This review aims to provide a background to the bone remodelling process, the bone repair cascade post-implantation, and the associated complications. Furthermore, current clinical solutions that can influence bone formation via either internal or extrinsic mechanisms will be described. These efficacious treatments for osteolysis via targeting the RANKL/OPG ratio may be crucial to reducing the incidence of related implant failures in the future.
Keywords: OPG; RANKL; bone; bone loss; bone regeneration; complications; implants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand (RANKL)/osteoprotegerin (OPG) ratio is increased in severe osteolysis.Am J Pathol. 2003 Nov;163(5):2021-31. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63560-2. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 14578201 Free PMC article.
-
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB ligand is expressed in resident and inflammatory cells in aseptic and septic prosthesis loosening.Scand J Rheumatol. 2003;32(5):287-94. doi: 10.1080/03009740310003929. Scand J Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 14690142
-
Dental and Orthopaedic Implant Loosening: Overlap in Gene Expression Regulation.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 11;13:820843. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.820843. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35222398 Free PMC article.
-
Role of receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand and osteoprotegerin in bone cell biology.J Mol Med (Berl). 2001 Jun;79(5-6):243-53. doi: 10.1007/s001090100226. J Mol Med (Berl). 2001. PMID: 11485016 Review.
-
Gene therapy methods in bone and joint disorders. Evaluation of the adeno-associated virus vector in experimental models of articular cartilage disorders, periprosthetic osteolysis and bone healing.Acta Orthop Suppl. 2007 Apr;78(325):1-64. Acta Orthop Suppl. 2007. PMID: 17427340 Review.
Cited by
-
Dual-functional composite scaffolds for inhibiting infection and promoting bone regeneration.Mater Today Bio. 2022 Aug 27;16:100409. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2022.100409. eCollection 2022 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2022. PMID: 36090611 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulation Pathogenesis and Treatment of Bone Nonunion.Orthop Surg. 2024 Aug;16(8):1770-1782. doi: 10.1111/os.14131. Epub 2024 Jun 30. Orthop Surg. 2024. PMID: 38946017 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of Biomarkers and Marginal Bone Loss in Platform-Switched and Nonplatform-Switched Implants: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Biomed Res Int. 2022 May 21;2022:2603287. doi: 10.1155/2022/2603287. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 35637753 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Topography-mediated immunomodulation in osseointegration; Ally or Enemy.Biomaterials. 2022 Dec;291:121903. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2022.121903. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Biomaterials. 2022. PMID: 36410109 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collagen Extract Derived from Yeonsan Ogye Chicken Increases Bone Microarchitecture by Suppressing the RANKL/OPG Ratio via the JNK Signaling Pathway.Nutrients. 2020 Jul 2;12(7):1967. doi: 10.3390/nu12071967. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32630655 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clough J. The Cleveland Clinic Guide to Arthritis. Kaplan Publishing; New York, NY, USA: 2009. p. 245.
-
- Gwinnutt J.M., Symmons D.P.M., MacGregor A.J., Chipping J.R., Lapraik C., Marshall T., Lunt M., Verstappen S.M.M. Predictors of and outcomes following orthopaedic joint surgery in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis followed for 20 years. Rheumatology. 2017;56:1510–1517. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex062.154. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

