Phase changes in neuronal postsynaptic spiking due to short term plasticity
- PMID: 28937977
- PMCID: PMC5627952
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005634
Phase changes in neuronal postsynaptic spiking due to short term plasticity
Abstract
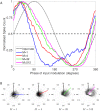
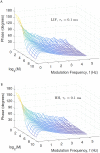
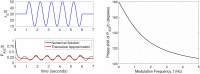
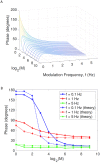
In the brain, the postsynaptic response of a neuron to time-varying inputs is determined by the interaction of presynaptic spike times with the short-term dynamics of each synapse. For a neuron driven by stochastic synapses, synaptic depression results in a quite different postsynaptic response to a large population input depending on how correlated in time the spikes across individual synapses are. Here we show using both simulations and mathematical analysis that not only the rate but the phase of the postsynaptic response to a rhythmic population input varies as a function of synaptic dynamics and synaptic configuration. Resultant phase leads may compensate for transmission delays and be predictive of rhythmic changes. This could be particularly important for sensory processing and motor rhythm generation in the nervous system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Estimating short-term synaptic plasticity from pre- and postsynaptic spiking.PLoS Comput Biol. 2017 Sep 5;13(9):e1005738. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1005738. eCollection 2017 Sep. PLoS Comput Biol. 2017. PMID: 28873406 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling the Short-Term Dynamics of in Vivo Excitatory Spike Transmission.J Neurosci. 2020 May 20;40(21):4185-4202. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1482-19.2020. Epub 2020 Apr 17. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32303648 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory synaptic plasticity regulates pyramidal neuron spiking in the rodent hippocampus.Neuroscience. 2008 Jul 31;155(1):64-75. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.05.009. Epub 2008 May 21. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18562122
-
Spike timing-dependent plasticity: from synapse to perception.Physiol Rev. 2006 Jul;86(3):1033-48. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00030.2005. Physiol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16816145 Review.
-
Spike timing dependent synaptic plasticity in biological systems.Biol Cybern. 2002 Dec;87(5-6):392-403. doi: 10.1007/s00422-002-0361-y. Biol Cybern. 2002. PMID: 12461629 Review.
Cited by
-
Flexible Spiking CPGs for Online Manipulation During Hexapod Walking.Front Neurorobot. 2020 Jun 26;14:41. doi: 10.3389/fnbot.2020.00041. eCollection 2020. Front Neurorobot. 2020. PMID: 32676022 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the dynamics of cerebellar Purkinje cells through the interaction of excitatory and inhibitory feedforward pathways.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Feb 10;17(2):e1008670. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008670. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 33566820 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of Cholinergic Circuits as an Area for Targeted Drug Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease: In Vivo Assessment of Short-Term Plasticity in Rat Brain.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020 Oct 9;13(10):297. doi: 10.3390/ph13100297. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33050228 Free PMC article.
-
Inter-Animal Variability in Activity Phase Is Constrained by Synaptic Dynamics in an Oscillatory Network.eNeuro. 2022 Jul 25;9(4):ENEURO.0027-22.2022. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0027-22.2022. Print 2022 Jul-Aug. eNeuro. 2022. PMID: 35817566 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Non-spiking Interneurons in Spiking Neural Networks.Front Neurosci. 2021 Mar 5;15:633945. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.633945. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33746701 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

