Body Composition Changes in Severely Burned Children During ICU Hospitalization
- PMID: 28938290
- PMCID: PMC5716837
- DOI: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000001347
Body Composition Changes in Severely Burned Children During ICU Hospitalization
Abstract
Objectives: Prolonged hospitalization due to burn injury results in physical inactivity and muscle weakness. However, how these changes are distributed among body parts is unknown. The aim of this study was to evaluate the degree of body composition changes in different anatomical regions during ICU hospitalization.
Design: Retrospective chart review.
Setting: Children's burn hospital.
Patients: Twenty-four severely burned children admitted to our institution between 2000 and 2015.
Interventions: All patients underwent a dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry within 2 weeks after injury and 2 weeks before discharge to determine body composition changes. No subject underwent anabolic intervention. We analyzed changes of bone mineral content, bone mineral density, total fat mass, total mass, and total lean mass of the entire body and specifically analyzed the changes between the upper and lower limbs.
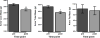
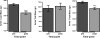
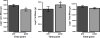
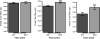
Measurements and main results: In the 24 patients, age was 10 ± 5 years, total body surface area burned was 59% ± 17%, time between dual-energy x-ray absorptiometries was 34 ± 21 days, and length of stay was 39 ± 24 days. We found a significant (p < 0.001) average loss of 3% of lean mass in the whole body; this loss was significantly greater (p < 0.001) in the upper extremities (17%) than in the lower extremities (7%). We also observed a remodeling of the fat compartments, with a significant whole-body increase in fat mass (p < 0.001) that was greater in the truncal region (p < 0.0001) and in the lower limbs (p < 0.05).
Conclusions: ICU hospitalization is associated with greater lean mass loss in the upper limbs of burned children. Mobilization programs should include early mobilization of upper limbs to restore upper extremity function.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Dr. Rivas disclosed that he does not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
The Quest to Preserve Muscle Mass-Lessons From Pediatric Burn Injury.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017 Dec;18(12):1186-1187. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000001358. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017. PMID: 29206739 No abstract available.
References
-
- Vet NJ, et al. Optimal sedation in pediatric intensive care patients: a systematic review. Intensive Care Med. 2013;39(9):1524–34. - PubMed
-
- Pereira C, et al. Post burn muscle wasting and the effects of treatments. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005;37(10):1948–61. - PubMed
-
- Schweickert WD, Hall J. ICU-acquired weakness. Chest. 2007;131(5):1541–9. - PubMed
-
- Gruther W, et al. Muscle wasting in intensive care patients: ultrasound observation of the M. quadriceps femoris muscle layer. J Rehabil Med. 2008;40(3):185–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

