Gonadotropin-Dependent Neuregulin-1 Signaling Regulates Female Rat Ovarian Granulosa Cell Survival
- PMID: 28938399
- PMCID: PMC5659703
- DOI: 10.1210/en.2017-00065
Gonadotropin-Dependent Neuregulin-1 Signaling Regulates Female Rat Ovarian Granulosa Cell Survival
Abstract
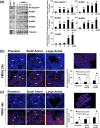
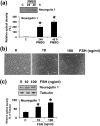
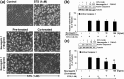
Mammalian ovarian follicular development and maturation of an oocyte competent to be fertilized and develop into an embryo depends on tightly regulated, spatiotemporally orchestrated crosstalk among cell death, survival, and differentiation signals through extra- and intraovarian signals, as well as on a permissive ovarian follicular microenvironment. Neuregulin-1 (NRG1) is a member of the epidermal growth factor-like factor family that mediates its effects by binding to a member of the erythroblastoma (ErbB) family. Our experimental results suggest gonadotropins promote differential expression of NRG1 and erbB receptors in granulosa cells (GCs), and NRG1 in theca cells during follicular development, and promote NRG1 secretions in the follicular fluid (FF) of rat ovaries. During the estrous cycle of rat, NRG1 and erbB receptors are differentially expressed in GCs and correlate positively with serum gonadotropins and steroid hormones. Moreover, in vitro experimental studies suggest that the protein kinase C inhibitor staurosporine (STS) causes the physical destruction of GCs by the activation of caspase-3. Exogenous NRG1 treatment of GCs delayed onset of STS-induced apoptosis and inhibited cleaved caspase-3 expressions. Moreover, exogenous NRG1 treatment of GCs alters STS-induced death by maintaining the expression of ErbB2, ErbB3, pAkt, Bcl2, and BclxL proteins. Taken together, these studies demonstrate that NRG1 is gonadotropin dependent, differentially regulated in GCs and theca cells, and secreted in ovarian FF as an intracellular survival factor that may govern follicular maturation.
Copyright © 2017 Endocrine Society.
Figures


References
-
- Havelock JC, Rainey WE, Carr BR. Ovarian granulosa cell lines. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2004;228(1-2):67–78. - PubMed
-
- Prochazka R, Blaha M, Nemcova L. Signaling pathways regulating FSH- and amphiregulin-induced meiotic resumption and cumulus cell expansion in the pig. Reproduction. 2012;144(5):535–546. - PubMed
-
- Ashkenazi H, Cao X, Motola S, Popliker M, Conti M, Tsafriri A. Epidermal growth factor family members: endogenous mediators of the ovulatory response. Endocrinology. 2005;146(1):77–84. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ami I, Armon L, Freimann S, Strassburger D, Ron-El R, Amsterdam A. EGF-like growth factors as LH mediators in the human corpus luteum. Hum Reprod. 2009;24(1):176–184. - PubMed
-
- Berasain C, Avila MA. Amphiregulin. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2014;28:31–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

