MiR-590-3p promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer via Hippo pathway
- PMID: 28938537
- PMCID: PMC5601633
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19487
MiR-590-3p promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer via Hippo pathway
Abstract
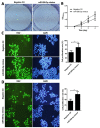
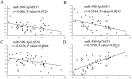
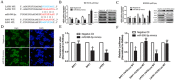
Studies reported that miR-590-3p was involved in human cancer progression. However, its roles of oncogene or anti-oncogene in malignancies still remain elusive. This study was aimed to investigate the effect of miR-590-3p on the cell proliferation and metastasis via Hippo pathway in colorectal cancer (CRC). In our study, miR-590-3p was demonstrated highly expressed in CRC tissues, compared with adjacent normal tissues (P<0.05). In addition, miR-590-3p was positively associated with TNM stage and distant metastasis. Survival analysis showed that high miR-590-3p was related with poor overall survival rate. Then, over-expressed miR-590-3p was demonstrated to promote proliferation, invasion and migration of colon caner cells. What's more, MST1, LATS1 and SAV1 mRNA were showed lowly expressed and YAP1 expression in mRNA and protein levels were highly expressed in CRC tissues, compared with adjacent normal tissues (all P<0.05). miR-590-3p expression was negatively associated with LATS1 and SAV1 mRNA respectively and positively related with YAP1 mRNA in CRC tissues, meanwhile, there was no relationship between miR-590-3p and MST1 mRNA. Furthermore, over-expressing miR-590-3p inhibited expressions of LATS1 and SAV1, promoted YAP1 expression and didn't effect MST1 expression in colon cancer cells. And luciferase assay showed that miR-590-3p over-expression inhibited the luciferase activity of LATS1 and SAV1 3'UTR, meanwhile it had no effect on the mutated form of these two plasmids. Taken together, these data suggest that highly-expressed miR-590-3p promotes biological effect of proliferation and metastasis via targeting Hippo pathway, and predicts worse clinical outcomes of CRC patients.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; colorectal cancer; metastasis; miR-590-3p; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MiR-103a-3p promotes tumour glycolysis in colorectal cancer via hippo/YAP1/HIF1A axis.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Nov 20;39(1):250. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01705-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33218358 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-490-3p inhibits colorectal cancer metastasis by targeting TGFβR1.BMC Cancer. 2015 Dec 29;15:1023. doi: 10.1186/s12885-015-2032-0. BMC Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26714817 Free PMC article.
-
miR-27a-3p targeting RXRα promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 26;8(47):82991-83008. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19635. eCollection 2017 Oct 10. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29137318 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of microRNA-103a-3p inhibits the malignancy of thyroid cancer cells through Hippo signaling pathway by upregulating LATS1.Neoplasma. 2020 Nov;67(6):1266-1278. doi: 10.4149/neo_2020_191224N1331. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Neoplasma. 2020. PMID: 32749848
-
MiR-22-3p regulates the proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by directly targeting KDM3A through the Hippo pathway.Histol Histopathol. 2022 Dec;37(12):1241-1252. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-526. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Histol Histopathol. 2022. PMID: 36173030
Cited by
-
Impaired Expression of the Salvador Homolog-1 Gene Is Associated with the Development and Progression of Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 8;15(24):5771. doi: 10.3390/cancers15245771. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38136317 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Regulation by lncRNAs: An Overview Focused on UCA1 in Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Nov 14;10(11):440. doi: 10.3390/cancers10110440. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30441811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Implications of miRNA-590 dysregulation in digestive tract malignancies: mechanistic aspects and clinical significance.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 5;52(1):551. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10656-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40471218 Review.
-
Differential expression of microRNAs in xenografted Lewis lung carcinomas subjected to intermittent hypoxia: a next-generation sequence analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Jul;9(7):4354-4365. doi: 10.21037/tcr-19-2913. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117801 Free PMC article.
-
A Pilot Investigation of Circulating miRNA Expression in Individuals Exposed to Aluminum and Welding Fumes.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025 Apr 26;47(5):306. doi: 10.3390/cimb47050306. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40699705 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dienstmann R, Salazar R, Tabernero J. Personalizing colon cancer adjuvant therapy: selecting optimal treatments for individual patients. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:1787–1796. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Miller KD, Fedewa SA, Ahnen DJ, Meester RG, Barzi A, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:177–193. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS, Jemal A. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:252–271. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

