MicroRNA-128-3p regulates mitomycin C-induced DNA damage response in lung cancer cells through repressing SPTAN1
- PMID: 28938540
- PMCID: PMC5601636
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.12300
MicroRNA-128-3p regulates mitomycin C-induced DNA damage response in lung cancer cells through repressing SPTAN1
Abstract
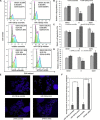
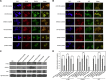
The DNA damage response is critical for maintaining genome integrity and preventing damage to DNA due to endogenous and exogenous insults. Mitomycin C (MMC), a potent DNA cross-linker, is used as a chemotherapeutic agent because it causes DNA inter-strand cross-links (DNA ICLs) in cancer cells. While many microRNAs, which may serve as oncogenes or tumor suppressors, are grossly dysregulated in human cancers, little is known about their roles in MMC-treated lung cancer. Here, we report that miR-128-3p can attenuate repair of DNA ICLs by targeting SPTAN1 (αII Sp), resulting in cell cycle arrest and promoting chromosomal aberrations in lung cancer cells treated with MMC. Using computational prediction and experimental validation, SPTAN1 was found to be a conserved target of miR-128-3p. We then found that miR-128-3p caused translational inhibition of SPTAN1, reducing its protein level. SPTAN1 repression via miR-128-3p also induced cell cycle arrest and chromosomal instability. Additionally, miR-128-3p significantly influenced interaction of the αII Sp/FANCA/XPF complex, thus limiting DNA repair. In summary, the results demonstrate that miR-128-3p accelerates cell cycle arrest and chromosomal instability in MMC-treated lung cancer cells by suppressing SPTAN1, and these findings could be applied for adjuvant chemotherapy of lung cancer.
Keywords: DNA repair; MicroRNA; lung cancer; mitomycin C; spectrin.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sculier JP, Ghisdal L, Berghmans T, Branle F, Lafitte JJ, Vallot F, Meert AP, Lemaitre F, Steels E, Burniat A, Mascaux C, European Lung Cancer Working P The role of mitomycin in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis of the literature. Br J Cancer. 2001;84:1150–1155. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bakowski MT, Crouch JC. Chemotherapy of non-small cell lung cancer: a reappraisal and a look to the future. Cancer Treat Rev. 1983;10:159–172. - PubMed
-
- Tomasz M, Palom Y. The mitomycin bioreductive antitumor agents: cross-linking and alkylation of DNA as the molecular basis of their activity. Pharmacol Ther. 1997;76:73–87. - PubMed
-
- Palom Y, Suresh Kumar G, Tang LQ, Paz MM, Musser SM, Rockwell S, Tomasz M. Relative toxicities of DNA cross-links and monoadducts: new insights from studies of decarbamoyl mitomycin C and mitomycin. C. Chem Res Toxicol. 2002;15:1398–1406. - PubMed
-
- Pasquinelli AE. MicroRNAs and their targets: recognition, regulation and an emerging reciprocal relationship. Nat Rev Genet. 2012;13:271–282. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

