Novel pleiotropic effects of bioactive phospholipids in human lung cancer metastasis
- PMID: 28938552
- PMCID: PMC5601648
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17461
Novel pleiotropic effects of bioactive phospholipids in human lung cancer metastasis
Abstract
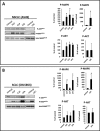
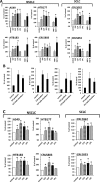
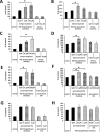
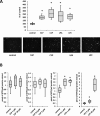
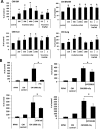
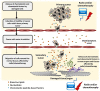
We previously proposed that one of the unwanted side effects of chemotherapy and radiotherapy is the increase in several peptide- and non-peptide based chemoattractants in damaged tissues, leading to induction of a prometastatic microenvironment for remaining cancer cells. Herein, we turned out our attention to a potential role of bioactive phospholipids (BphsLs), such as sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), ceramide-1-phosphate (C1P), lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) in lung cancer (LC) metastasis. We report that LC cells express several functional BphL receptors (for S1P, LPC, and LPA) as well as several enzymes involved in their metabolism and that BphsLs are potent chemokinetic and adhesion factors for these cells. We also demonstrate for the first time the novel role of C1P as a prometastatic factor in LC cells. In addition to their chemokinetic activities, BphsLs also sensitize or prime the chemotactic responsiveness of LC cells to known prometastatic factors such as hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor (HGF/SF). Thus, for the first time we demonstrate a prometastatic effect that is based on the priming of a cell's responsiveness to chemotactic factors by chemokinetic factors. To our surprise, none of the bioactive lipids induced proliferation of LC cells or ameliorated toxic effects of vincristine treatment. Interestingly, BphsLs increase adhesion of LC cells to bone marrow-derived stromal cells and stimulate these cells to release ExNs, which additionally increase LC cell motility. In conclusion, our results show that BphsLs are important modulators of prometastatic environment. Therefore, their inhibitors could be considered as potential anti-metastatic drug candidates to be included as a part of post radio- and/or chemo- therapy treatment.
Keywords: HGF/SF; bioactive phospholipids; lung cancer; metastasis; priming.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST Authors declare no conflicts of interest
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bioactive lipids S1P and C1P are prometastatic factors in human rhabdomyosarcoma, and their tissue levels increase in response to radio/chemotherapy.Mol Cancer Res. 2013 Jul;11(7):793-807. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-12-0600. Epub 2013 Apr 24. Mol Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23615526 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive lipids, LPC and LPA, are novel prometastatic factors and their tissue levels increase in response to radio/chemotherapy.Mol Cancer Res. 2014 Nov;12(11):1560-73. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0188. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Mol Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25033840 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular nucleotides as novel, underappreciated pro-metastatic factors that stimulate purinergic signaling in human lung cancer cells.Mol Cancer. 2015 Nov 24;14:201. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0469-z. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26597723 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid phosphate phosphatases and related proteins: signaling functions in development, cell division, and cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2004 Aug 1;92(5):900-12. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20126. J Cell Biochem. 2004. PMID: 15258914 Review.
-
Targeting the lipids LPA and S1P and their signalling pathways to inhibit tumour progression.Expert Rev Mol Med. 2007 Oct 15;9(28):1-18. doi: 10.1017/S1462399407000476. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2007. PMID: 17935635 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-374b mediates the initiation of non-small cell lung cancer by regulating ITGB1 and p53 expressions.Thorac Cancer. 2020 Jun;11(6):1670-1678. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.13457. Epub 2020 May 4. Thorac Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32364676 Free PMC article.
-
Ceramide synthase 6 impacts T-cell allogeneic response and graft-versus-host disease through regulating N-RAS/ERK pathway.Leukemia. 2022 Jul;36(7):1907-1915. doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01581-6. Epub 2022 May 5. Leukemia. 2022. PMID: 35513703 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of an acid sphingomyelinase ceramide kinase pathway in the regulation of the chemokine CCL5.J Lipid Res. 2018 Jul;59(7):1219-1229. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M084202. Epub 2018 May 3. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 29724781 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of hsa-miR-125b-5p Interaction with S1P/Ceramide Axis in the Potential Development of Inflammation-Associated Colon Cancer in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 24;24(11):9175. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119175. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298127 Free PMC article.
-
The Nlrp3 inflammasome as a "rising star" in studies of normal and malignant hematopoiesis.Leukemia. 2020 Jun;34(6):1512-1523. doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-0827-8. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Leukemia. 2020. PMID: 32313108 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ries LAG, Eisner MP, Kosary CL, Hankey BF, Miller BA, Clegg L, Mariotto A, Feuer EJ, BKe Edwards. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2002, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD: http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2002/ Last accessed January, 17.
-
- Maulik G, Kijima T, Ma PC, Ghosh SK, Lin J, Shapiro GI, Schaefer E, Tibaldi E, Johnson BE, Salgia R. Modulation of the c-Met/hepatocyte growth factor pathway in small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:620–7. - PubMed
-
- Fridlender ZG, Kapoor V, Buchlis G, Cheng G, Sun J, Wang LC, Singhal S, Snyder LA, Albelda SM. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 blockade inhibits lung cancer tumor growth by altering macrophage phenotype and activating CD8+ cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;44:230–7. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0080OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

